ChatGPT Speeds Up Patient Interview Analysis with Human Oversight
ChatGPT 4.0 boosts analysis efficiency in qualitative research, offering significant time savings. However, it still requires human expertise to refine results and capture subtle patient insights.
In an article published in the journal Nature Eye, researchers compared the efficiency and theme-identification accuracy of chat generative pre-trained transformers (ChatGPT) (versions 3.5 and 4.0) with traditional human analysis in processing patient interview transcripts from a community eye clinic. Results showed ChatGPT significantly reduced analysis time with moderate to high theme concordance, suggesting it could support rapid, preliminary qualitative analysis, though final theme refinement remains necessary by human researchers.
The study involved three diverse patients with different eye conditions (glaucoma, cataracts, and macular degeneration), ensuring the results were applicable to a variety of healthcare contexts.
The Role of ChatGPT in Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is essential for gaining insights into complex, real-world issues by capturing participants' experiences and perspectives. While valuable, this approach is often resource-intensive due to time-consuming steps like data collection, transcription, and analysis.
Previous studies report substantial labor and costs, with transcription alone consuming hours per interview and incurring thousands in expenses. To address these challenges, artificial intelligence (AI) showed potential to streamline qualitative analysis. ChatGPT, OpenAI’s language model, emerged as a promising tool for efficiently processing and analyzing large datasets.

Evaluating ChatGPT 4.0 in Qualitative Data Analysis
Earlier research by De Paoli demonstrated ChatGPT 3.5’s ability to identify themes from interview transcripts but didn’t assess ChatGPT 4.0’s capabilities. This paper built on prior findings by comparing ChatGPT versions 3.5 and 4.0 to traditional analysis and evaluating both their speed and accuracy in theme identification.
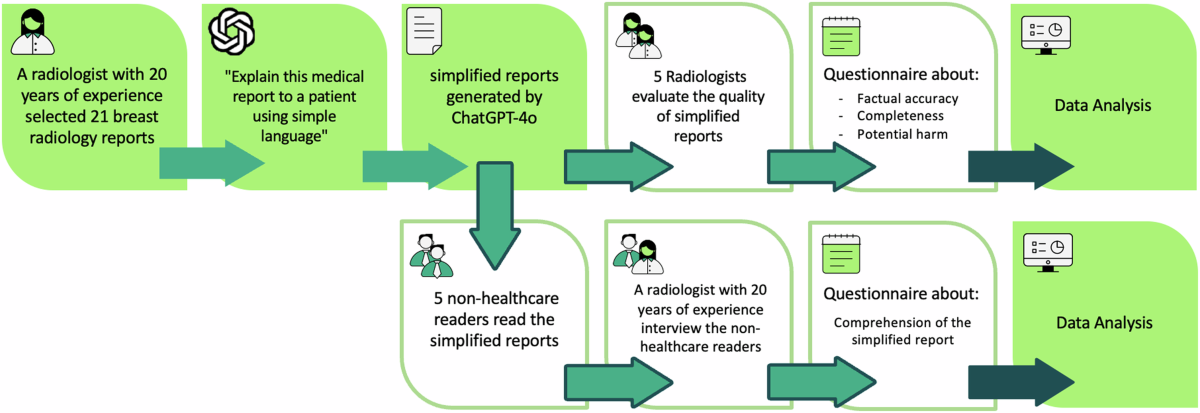
The authors evaluated the use of ChatGPT 3.5 and 4.0 in analyzing qualitative data from in-depth interviews on patient experiences at a community clinic. Three anonymized transcripts were selected, and themes were coded manually by researchers, who developed a working codebook through iterative analysis.
Accuracy and Efficiency of ChatGPT
To assess the accuracy of ChatGPT's thematic analysis, the researchers calculated concordance by comparing ChatGPT-generated themes with their manually established themes. The findings indicated that ChatGPT significantly reduced analysis time, averaging 11.5-11.9 minutes per transcript compared to 240 minutes for manual analysis. ChatGPT 3.5 achieved an 83.5% concordance, while ChatGPT 4.0 showed similar concordance, with fewer unrelated subthemes.
The researchers suggested that ChatGPT could streamline qualitative analysis, though additional refinement by researchers was necessary. Ethical approval was granted, and informed consent was obtained from all interview participants.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite AI's efficiency, it struggled with nuanced themes like patient emotions and implicit contexts, highlighting the importance of human involvement in complex qualitative analysis. While both ChatGPT versions demonstrated similar concordance (83.7%) with the researcher-generated themes, ChatGPT 4.0 generated fewer irrelevant subthemes than ChatGPT 3.5, potentially indicating improved contextual relevance.
Despite ChatGPT’s efficiency, limitations remained in its capacity to capture deeper emotions and implicit themes, which a human researcher would likely discern. For example, irrelevant subthemes such as "contact lens prescription" and "personal history of chronic conditions" were flagged by ChatGPT as unrelated.
Future studies should focus on refining prompts to better guide AI models and ensure data accuracy through human researchers' cross-referencing. The combined use of ChatGPT with transcription tools like Whisper could further reduce costs, making qualitative research more accessible and relevant for healthcare improvement.
In conclusion, the researchers highlighted ChatGPT’s potential as a valuable tool for streamlining qualitative data analysis. It offers significant time savings and moderate to good concordance with human-generated themes. While ChatGPT could support rapid, preliminary analysis, human involvement remained essential for interpreting nuanced themes and ensuring accuracy. Future refinements, including tailored prompts and enhanced cross-checking, may further improve ChatGPT’s applicability in qualitative healthcare research.
Posted in: AI Research News
Tags: Artificial Intelligence, Data Analysis, Healthcare, Training Data




















