Your Brain Works Backwards—and Not the Way You Think ...
Imagine you’re at your favorite coffee shop. Sadly, the barista only gets your order right about 75% of the time. According to most neuroscience research before 2025, your brain should release rewarding and comforting neurotransmitters like dopamine in direct proportion to that 75% success rate. What does this mean? Well, a few things.
First, you think your brain is cued to feel satisfied three out of four times through a predictable neural response. Secondly, when the order is wrong, you get disappointed, frustrated, or even angry. But surprise, that's not how your brain actually works! Thinking is not that simple. Your mind doesn't just ponder success probabilities. You focus more on the beliefs you have about how the world works, than you do about pure math.
For parents and educators: Stop relying on random rewards based on mood! Children will respond completely differently to predictable rewards for specific achievements versus surprise rewards with no clear connection to behavior. Structure uncertainty carefully—some unpredictability motivates, but too much chaos shuts down learning entirely.
Belief States and Brain Function
What's really happening is a perpetual updating of what you expect to happen (the hot coffee reward) based on so much more than probability. Instead, your brain creates "belief states,"—meaning your brain runs multiple scenario simulations simultaneously and bases its neurological responses based on those complex mental models (Qian et al., 2025).
Implications on Motivation and Learning
This discovery matters because it changes everything we thought we know about motivation, learning, and why some rewards work while others fall flat. What it really means is that two situations with identical reward probabilities can trigger completely different dopamine responses depending on your brain's current "belief state" about what's happening.
Neurological Responses to Predictions
When the barista is making your drink, your brain isn't just thinking "75% success rate." It's running full-scale scenario simulations in the background. Each scenario gets a probability weight, and your dopamine response is based on this complex coffee cocktail of beliefs—not just raw statistics. Ultimately, how you feel depends on the accuracy of your prediction.
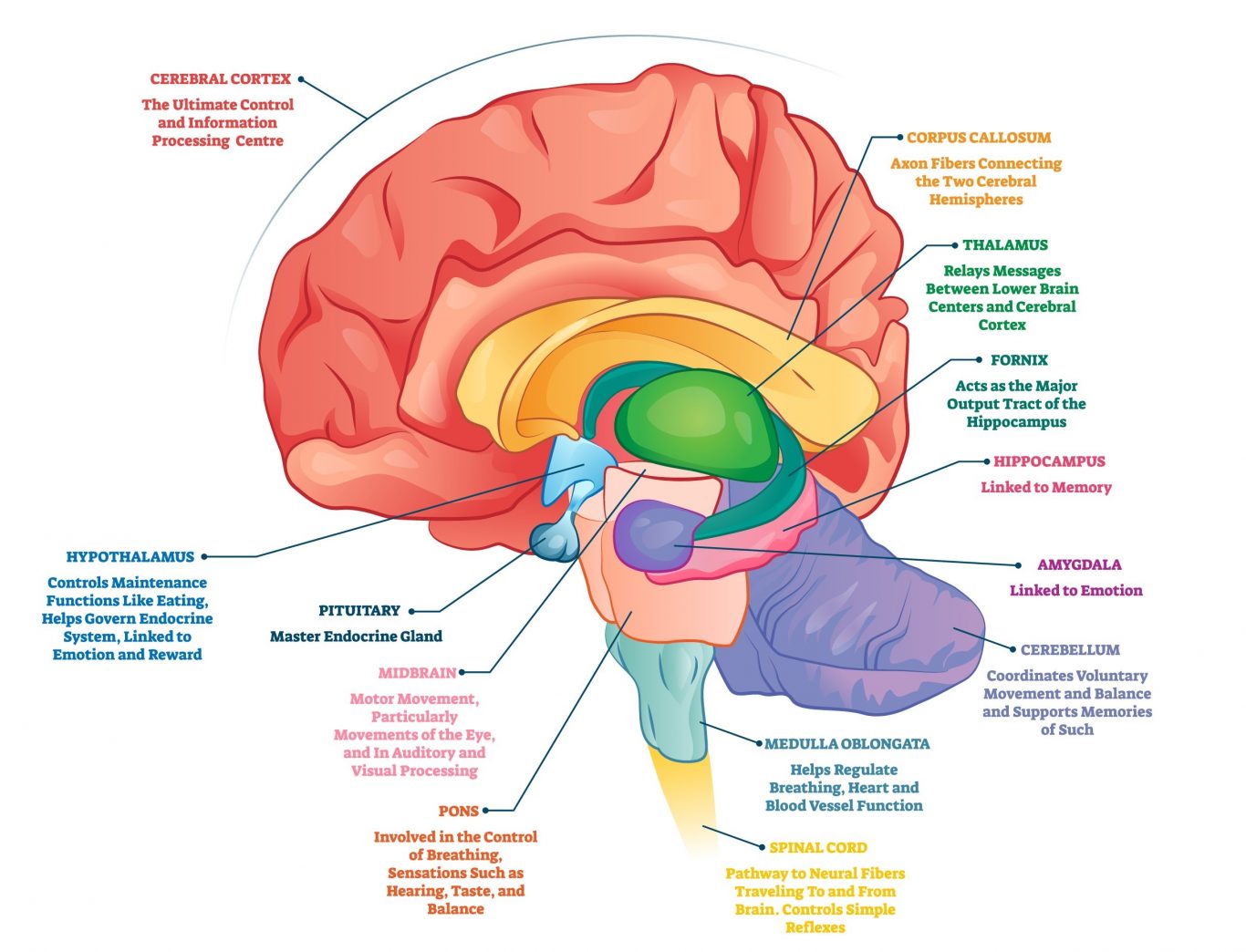
The Role of Dopamine Neurons
Dopamine neurons operate with a crucial asymmetry. They have an incredibly low baseline firing rate, but when something unexpectedly good happens, they can explode in activity. Context changes everything.
Implications for Behavior and Learning
When rewards come with clear signals, your brain processes the scenario differently than with no clear connection to behavior. This explains why some motivational strategies work brilliantly while others backfire spectacularly.
For personal development: Understanding rewards revolutionizes goal setting. Don't just celebrate successes—make sure your brain recognizes the reward as worthy and earned, not lucky.
For mental health: The research offers new hope for understanding depression and addiction. Rather than just chemical imbalances, these conditions might involve "stuck" belief states that don't update appropriately when circumstances change.
So how can you use this knowledge? The secret isn't to outsmart your dopamine system—it's to work with it. Build clear connections between effort and outcomes. Signal when good things are earned versus lucky. Regulate responses to both disappointment and success, so neither creates a neurological imbalance and puts you out of what I call “Momeostatis.” Create contexts where your brain can build accurate, updated mental models based on reality.
And maybe next time, make your own coffee. If it tastes good, you will get the dopamine hit. Finally, don’t blame the barista, blame your expectations!




















