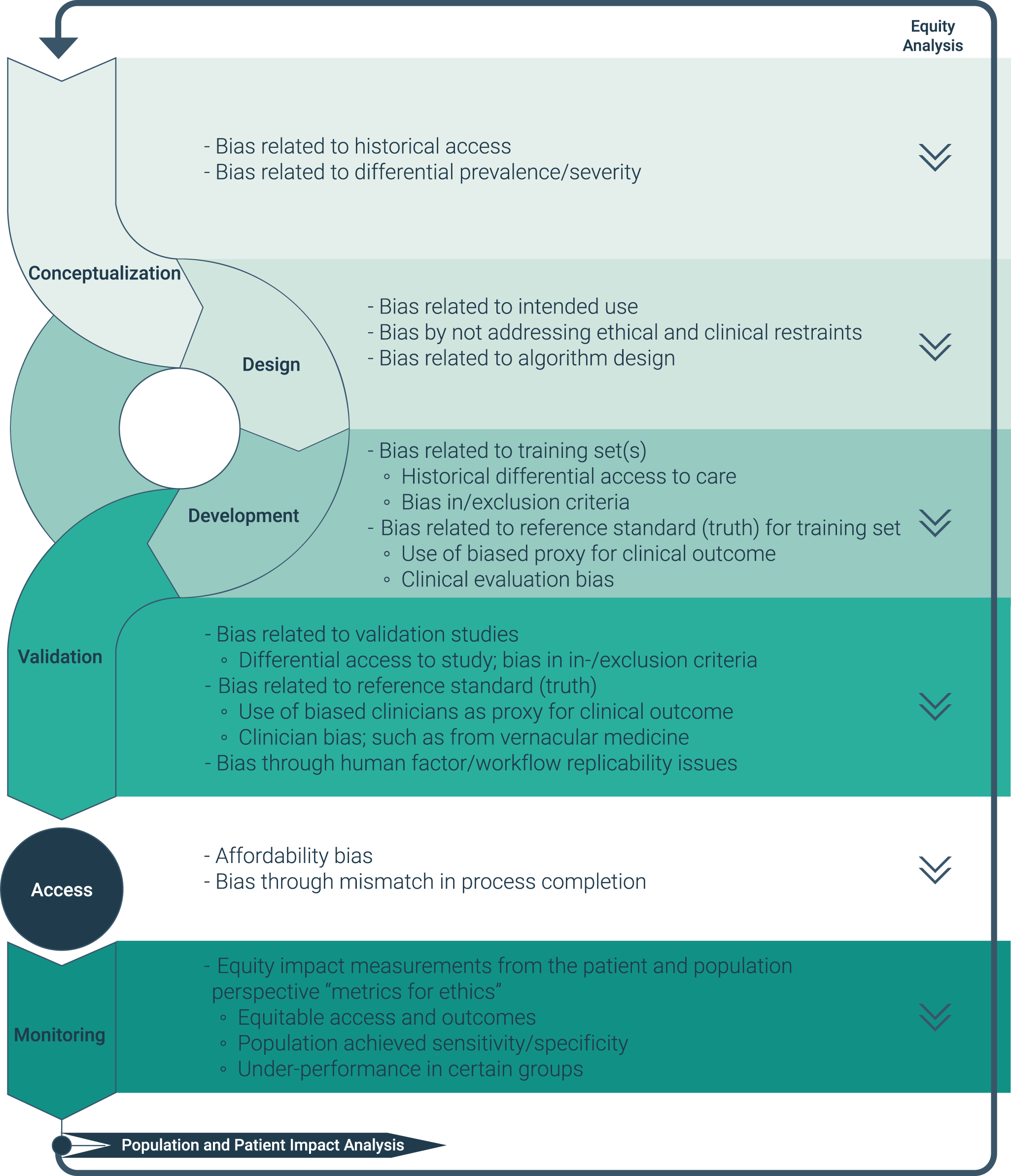
Major AI chatbots parrot CCP propaganda
Leading AI chatbots are reproducing Chinese Communist Party (CCP) propaganda and censorship when questioned on sensitive topics. According to the American Security Project (ASP), the CCP’s extensive censorship and disinformation efforts have contaminated the global AI data market. This infiltration of training data means that AI models – including prominent ones from Google, Microsoft, and OpenAI – sometimes generate responses that align with the political narratives of the Chinese state.
AI Chatbots Analysis
Investigators from the ASP analysed the five most popular large language model (LLM) powered chatbots: OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Microsoft’s Copilot, Google’s Gemini, DeepSeek’s R1, and xAI’s Grok. They prompted each model in both English and Simplified Chinese on subjects that the People’s Republic of China (PRC) considers controversial.
Every AI chatbot examined was found to sometimes return responses indicative of CCP-aligned censorship and bias. The report singles out Microsoft’s Copilot, suggesting it “appears more likely than other US models to present CCP propaganda and disinformation as authoritative or on equal footing with true information”. In contrast, X’s Grok was generally the most critical of Chinese state narratives.

Dataset Challenges
The root of the issue lies in the vast datasets used to train these complex models. LLMs learn from a massive corpus of information available online, a space where the CCP actively manipulates public opinion. Through tactics like “astroturfing,” CCP agents create content in numerous languages by impersonating foreign citizens and organisations. This content is then amplified on a huge scale by state media platforms and databases. The result is that a significant volume of CCP disinformation is ingested by these AI systems daily, requiring continuous intervention from developers to maintain balanced and truthful outputs.
Challenges for Companies
For companies operating in both the US and China, such as Microsoft, impartiality can be particularly challenging. The PRC has strict laws mandating that AI chatbots must “uphold core socialist values” and “actively transmit positive energy,” with severe consequences for non-compliance. The report notes that Microsoft, which operates five data centres in mainland China, must align with these data laws to retain market access. Consequently, its censorship tools are described as being even more robust than its domestic Chinese counterparts, scrubbing topics like the “Tiananmen Square,” the “Uyghur genocide,” and “democracy” from its services.
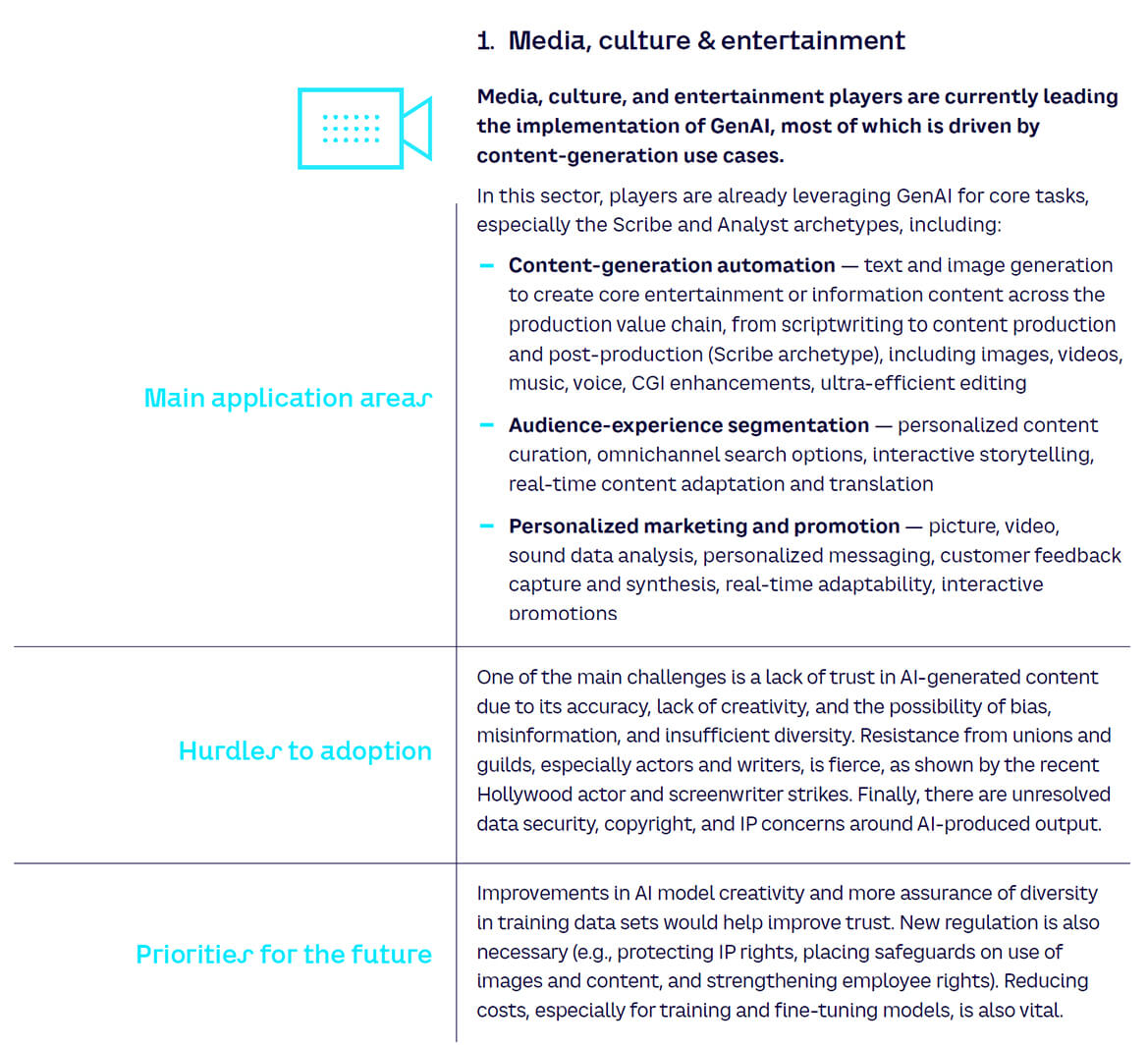
Language Discrepancies
The investigation revealed significant discrepancies in how the AI chatbots responded depending on the language of the prompt. When asked in English about the origins of the COVID-19 pandemic, ChatGPT, Gemini, and Grok outlined the most widely accepted scientific theory of a cross-species transmission from a live animal market in Wuhan, China. These models also acknowledged the possibility of an accidental lab leak from the Wuhan Institute of Virology, as suggested by a US FBI report. However, DeepSeek and Copilot gave more ambiguous answers, stating there was an ongoing scientific investigation with “inconclusive” evidence and did not mention either the Wuhan market or the lab leak theory.
In Chinese, the narrative shifted dramatically. All the LLMs described the pandemic’s origin as an “unsolved mystery” or a “natural spillover event”. Gemini went further, adding that “positive test results of COVID-19 were found in the US and France before Wuhan”.
Conclusion
The investigation concludes that expanding access to reliable and verifiably true AI training data is now an “urgent necessity”. The authors caution that if the proliferation of CCP propaganda continues while access to factual information diminishes, developers in the West may find it impossible to prevent the “potentially devastating effects of global AI misalignment”.