Introduction
Artificial Intelligence has seen remarkable advancements in recent years, particularly in natural language processing. Among the numerous AI language models, two have garnered significant attention: GPT-4 and Llama 3.1. Both are designed to understand and generate human-like text, making them valuable tools for various applications, from customer support to content creation.
Overview of ChatGPT-4 and Llama 3.1
In this blog, we will explore the differences and similarities between GPT-4 and Llama 3.1, delving into their technological foundations, performance, strengths, and weaknesses. By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of these two AI giants and insights into their prospects.
Introduction to GPT-4
ChatGPT, developed by OpenAI, represents one of the most advanced iterations in the series of Generative Pre-trained Transformers (GPT) models. The journey began with GPT-1, released in 2018, marking a significant milestone in the field of natural language processing (NLP). GPT-1 was built with 117 million parameters, setting the stage for more sophisticated models by showcasing the potential of transformer-based architectures in generating human-like text.
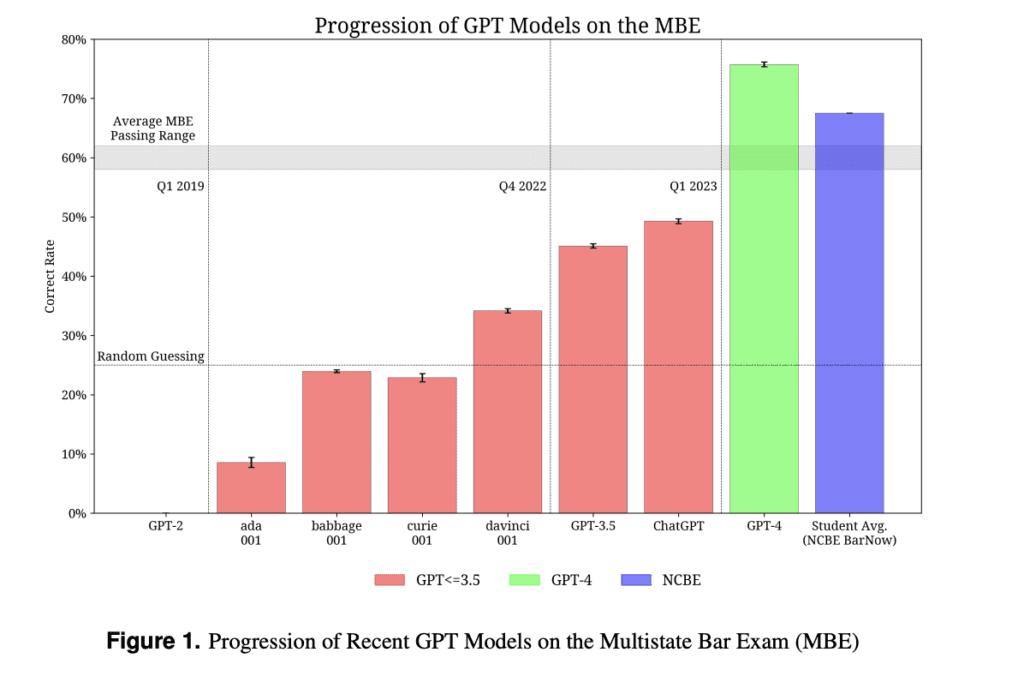
In this blog, we will explore the differences and similarities between GPT-4 and Llama 3.1, delving into their technological foundations, performance, strengths, and weaknesses. By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of these two AI giants and insights into their prospects.
Llama 3.1 Overview
Llama 3.1 is another prominent language model developed to push the boundaries of AI language capabilities. Created by Meta, Llama aims to provide a robust alternative to models like ChatGPT. Its development history is marked by a collaborative approach, drawing on the expertise of multiple institutions to create a model that excels in various language tasks.
Performance Comparison
One of the primary metrics for evaluating AI language models is their ability to understand and generate text. GPT-4 excels in generating coherent and contextually relevant responses, thanks to its extensive training data and large parameter count. It can handle a wide range of topics and provide detailed answers, making it a versatile tool for various applications.

Llama 3.1, while not as large as GPT-4, compensates with its efficiency and optimized performance. It has demonstrated strong capabilities in understanding and generating text, particularly in specific domains where it has been fine-tuned. Llama 3.1’s ability to provide accurate and context-aware responses makes it a valuable asset for targeted applications.
Strengths and Weaknesses
Llama 3.1 excels in contextual understanding and knowledge retrieval, making it a powerful tool for specialized applications. On the other hand, GPT-4 shines in conversational flow and creative writing, offering natural and engaging responses across a wide range of tasks.
Despite its strengths, Llama 3.1 has limitations, particularly in areas requiring common sense or understanding idiomatic expressions. On the other hand, GPT-4’s overconfidence and occasional lack of domain-specific knowledge can lead to challenges in certain applications.
.png)
Conclusion
Comparing GPT-4 and Llama 3.1 across different tasks highlights their respective strengths and weaknesses, offering a deeper understanding of their capabilities. The choice between these models depends on the specific use case.










