Why ChatGPT, Gemini, Grok face trademark registration hurdles in India
Global tech giants such as OpenAI, X.AI Corp, and Google are encountering challenges in securing trademark protection for their leading artificial intelligence (AI) brands like ChatGPT, Grok, and Gemini in India. The Indian Trade Marks Registry has raised flags on their applications or faced opposition from local entities, citing reasons such as prior use, confusing similarity, and bad faith adoption.
Classification Issues
Most trademark applications for AI models, including ChatGPT, Claude, Grok, Gemini, and Deep Seek, have been submitted under Class 9. This class covers downloadable software, artificial intelligence programs, data processing systems, and related digital tools, commonly used for trademarks associated with computer software and technological products.

Conflicts and Oppositions
Due to the overlapping classification, there is a higher chance of similar marks being reviewed together for potential conflicts under statutory provisions like Section 11 of the Trade Marks Act, 1999, which deals with relative grounds for refusal.
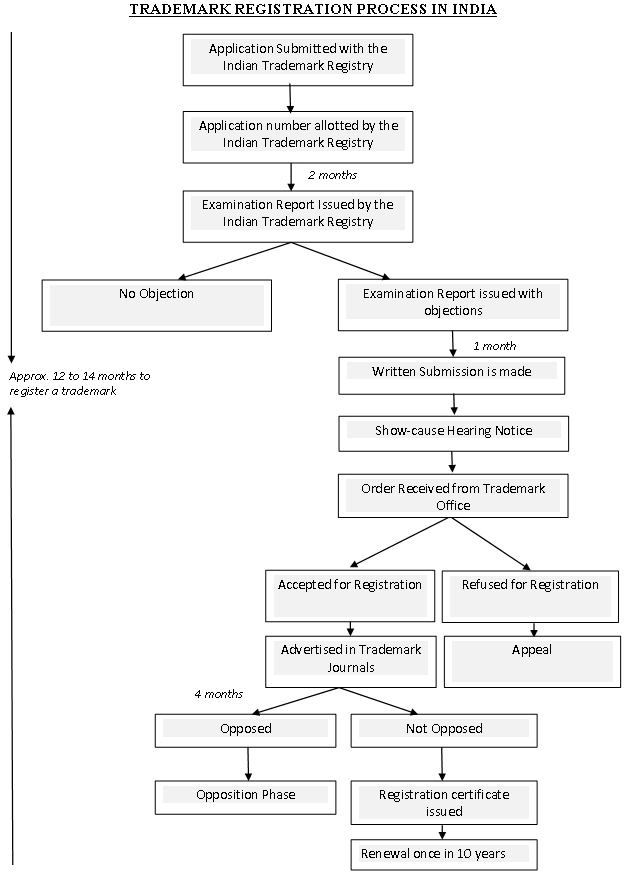
Trademark Registration Process
The standard registration process involves filing the application, examination by the Registry, responding to objections under Section 9 or Section 11 of the Trade Marks Act, a show cause hearing if necessary, advertisement in the Trade Marks Journal, a 4-month opposition window, and registration if no opposition is filed or if the opposition is overcome.
Case Studies
OpenAI's ChatGPT trademark is facing opposition from Flaxxi AI Private Limited, citing prior use in edtech services and the likelihood of confusion. Similarly, X's attempt to register "Grok" was met with a provisional refusal due to an existing mark, "Groke". Google's application for "Gemini" was objected to by Sun TV's "Gemini TV" trademarks, highlighting the challenges faced by these tech giants in the Indian market.
Multi-Party Disputes
Multiple entities applying for similar marks like Deep Seek indicate potential ownership disputes, leading to delays in registration. The Indian trademark law requires applicants to establish prior use, distinctiveness, or honest concurrent use in such scenarios.
Successful Registrations
Despite the obstacles, Anthropic's AI model Claude and Perplexity AI managed to secure trademark registrations in India without reported opposition, showcasing successful clearance through the registration process.

These examples shed light on the complexities faced by tech companies in trademark registrations in India.




















