The Evolution of AI: From Theories to ChatGPT
Artificial intelligence is often perceived as a modern wonder, yet its origins can be traced back to the mid-20th century when forward-thinking individuals dared to ponder: Can machines think? This daring question set off an evolution of AI that now permeates every facet of our lives. What was once confined to folklore and science fiction has slowly materialized over years of scientific inquiry and technological innovation.
The history of machine learning reflects this journey, marked by ambitious trials, grandiose assurances, and insightful lessons drawn from early setbacks. However, the timeline of AI progress demonstrates a steady advancement, from initial neural networks and rudimentary problem-solving algorithms to breakthroughs in natural language processing that enable computers to comprehend human speech.
The emergence of OpenAI's early language models served as a pivotal juncture in this narrative. With the introduction of GPT models, especially GPT-3 boasting 175 billion parameters, these models showcased more than sheer computational power - they exhibited a profound understanding of language. These models gleaned insights from vast datasets, swiftly adapted to new tasks with minimal direction, and offered responses that eerily resembled human speech patterns.
Key Milestones in AI Development
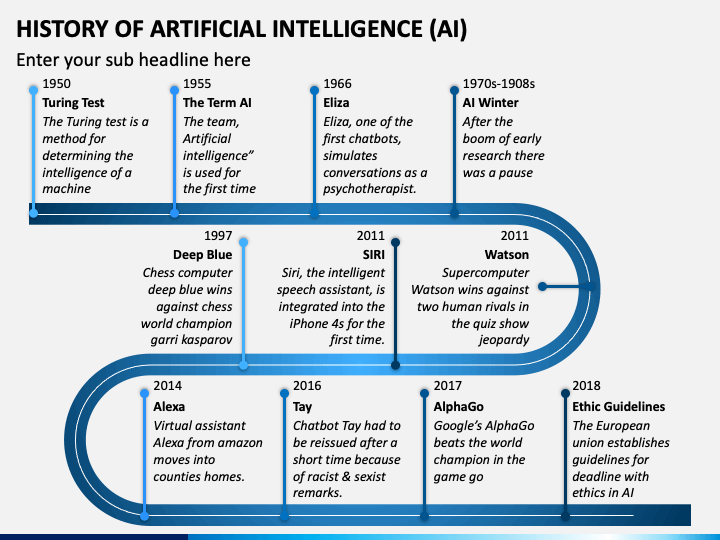
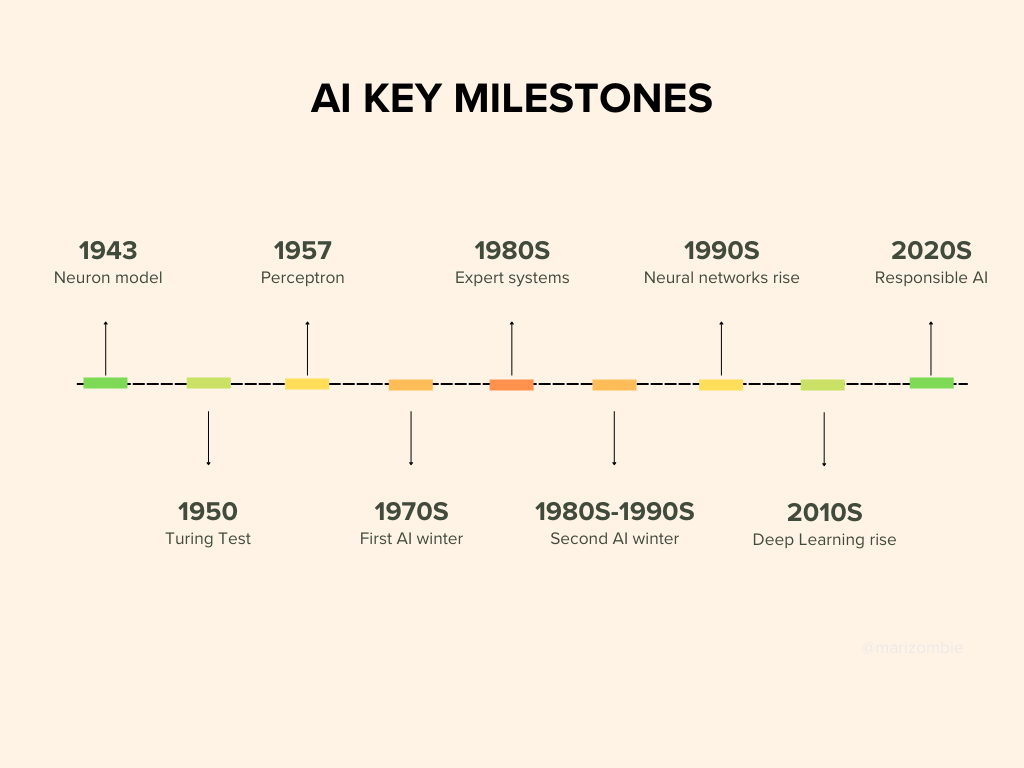
1950: Alan Turing put forth the notion of machine intelligence through his groundbreaking Turing Test, adopting a behavioral approach to delineate intelligent actions.
1951–1952: Christopher Strachey crafted one of the earliest successful AI programs for checkers; Anthony Oettinger's Shopper showcased basic learning capabilities.
1956: John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, and others convened the Dartmouth Conference, formally inaugurating AI as a distinct research domain.
1950s–1960s: The development of the Logic Theorist and General Problem Solver underscored AI's early emphasis on symbolic reasoning and rule-based issue resolution.
The Transition to Modern AI
The presence of AI in ubiquitous tools such as search engines, communication platforms, and productivity applications attests to the field's remarkable progression. However, to fully comprehend the future trajectory of this technology, a retrospective analysis of its evolution is imperative. The genesis of intelligent systems did not stem from silicon chips; rather, it sprouted from human inquisitiveness and creativity.
The odyssey of AI spans decades of experimentation, commencing with foundational theories and blossoming into sophisticated learning mechanisms, neural constructs, and real-world robotics.
In 1986, David Rumelhart and James McClelland trained a neural network to conjugate English verbs, showcasing the capacity of neural systems to generalize language patterns. This paved the way for the expansion of neural networks into diverse domains such as speech recognition, financial modeling, medical diagnostics, and visual perception.
Reimagining AI
In the 1990s and beyond, situated AI transitioned from abstract concepts to practical models capable of perceiving and reacting to their surroundings in real-time, prioritizing direct sensory inputs over memory-intensive logic mechanisms.
The narrative of AI transformation is interwoven with the contributions of visionaries like Alan Turing, John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, and others who reshaped the course of AI history with their seminal ideas and innovations.
Legacy of AI Pioneers
Key figures such as Alan Turing, John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, Herbert A. Simon, Allen Newell, Arthur Samuel, Frank Rosenblatt, Rodney Brooks, and Bert Dreyfus left an indelible mark on the trajectory of artificial intelligence. Their pioneering work laid the groundwork for the modern AI landscape we inhabit today.

Exploring AI Through Turing's Lens
Alan Turing's visionary concepts laid the groundwork for artificial intelligence long before the advent of contemporary computing. His theoretical model, the universal Turing machine, envisaged a machine capable of storing, processing, and adapting instructions akin to human memory, foreshadowing the dawn of machine learning.
Turing's musings on adaptive learning and heuristic problem-solving during WWII foreshadowed a future where machines could improve through experiential learning. His 1947 discourse on machine learning and the unpublished 1948 report on Intelligent Machinery foreshadowed methodologies that would later shape the field of AI.
AI in Practice: From Theory to Reality
The advent of practical AI applications in the early 1950s marked a pivotal shift, as programmers endeavored to construct machines capable of gameplay and experiential learning. Notable projects, including Christopher Strachey's checkers program and Anthony Oettinger's Shopper, demonstrated the feasibility of decision-making based on memory and logic.
Arthur Samuel's pioneering work in teaching a computer to enhance its checker gameplay exemplified a new phase in machine learning. His program's triumph over a state-level champion underscored the potential of evolving AI systems.
Insights from AI Progression
Turing's heuristic problem-solving approach laid the foundation for future AI advancements, culminating in breakthroughs such as IBM's Deep Blue defeating world chess champion Garry Kasparov in 1997. The evolution of AI from theoretical concepts to practical applications underscores the transformative power of human ingenuity and technological innovation.

From symbolic reasoning to neural networks and natural language processing, the evolution of AI has been a testament to human creativity and resilience in the face of computational challenges. As we navigate the complex terrain of AI development, it is crucial to reflect on the past to chart a course towards an AI-infused future.




















