What I Read This Week… - Chamath Palihapitiya
Read our Short Dive: The Trump Administration’s Fiscal Strategy
Read our Interview with Jason about the Evolution of Media
Caught My Eye…
Crypto acquisitions and public listings in the U.S. reached $8.2 billion across 88 transactions in the first four months of 2025, already tripling the total value of all 2024 crypto deal-making. These transactions reflect five distinct deal patterns:
- Bitcoin treasury acquisitions, where companies like Twenty One Capital are accumulating bitcoin as their primary business model, converting corporate treasuries into bitcoin investment vehicles to capitalize on cryptocurrency appreciation (similar to MicroStrategy).
- Mergers between traditional financial companies and crypto infrastructure companies, such as DTCC’s acquisition of Securrency, enabling traditional financial institutions to offer cryptocurrency services to clients who want exposure to both asset classes on a single platform.
- Institutional service acquisitions, such as Ripple's purchase of Metaco, which is intended to create specialized platforms that help professional investors securely store and manage digital assets with the compliance features required by large institutions.
- Consolidation of crypto exchanges, including Kraken's $1.5 billion purchase of futures broker NinjaTrader, as crypto platforms acquire traditional brokerages to create seamless trading between digital and conventional assets, allowing users to move effortlessly between different asset classes.
- On-chain mergers between token-based projects, such as the merger of Fetch.ai, Ocean Protocol, and SingularityNET, to combine user bases and offerings and accelerate the capture of network effects for their tokens.
Collectively, these transactions may bridge the gap between traditional finance and decentralized finance, driving institutional adoption while creating a more integrated cryptocurrency ecosystem.
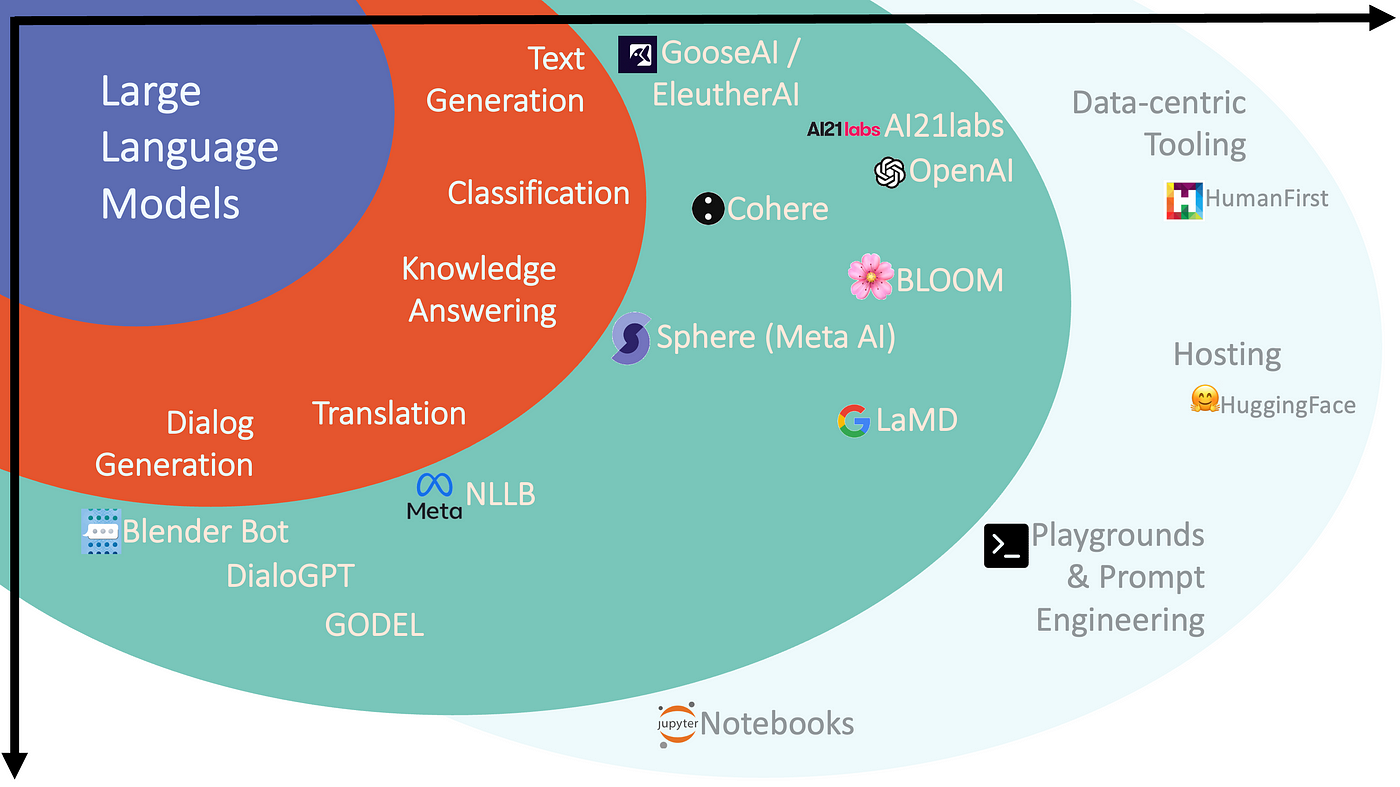
Language model providers are diverging in their model features and the ecosystems they are building, reflecting fundamentally different bets. For example, just between OpenAI and Google, OpenAI has the leading brand today, as ChatGPT has become synonymous with AI chatbots, while Google’s Gemini models have a cost advantage through their custom TPUs over ChatGPT, which runs on Nvidia GPUs. Gemini prioritizes massive context windows and reliability, while ChatGPT emphasizes complex reasoning and dynamic tool use. Google is creating an AI ecosystem that integrates with its broader suite of services, including Search, Gmail, Docs, and YouTube, and is advancing multimodal capabilities through DeepMind. By contrast, OpenAI is focusing on a standalone product experience that blends chat, document analysis, coding, and image generation, extended through Microsoft Azure and third-party plug-ins. Their approaches reflect two different bets: Google is integrating AI into the existing fabric of the internet and digital services, while OpenAI is building a standalone platform that users interact with directly.
About 28% of planned renewable energy projects originally slated to come online in 2024 have been delayed or canceled, representing 42,000 megawatts of capacity. Equipment shortages have led to multi-year wait times for turbines and transformers, with deliveries now taking an estimated three to six years. Manufacturers such as GE Vernova have stopped taking new orders after determining they cannot increase production capacity quickly enough to meet demand, while companies like Mitsubishi Power are reviewing their projects to potentially cancel more. At the same time, the cost of building new gas-fired power plants has more than tripled, rising from $785 per kilowatt in 2022 to $2,400 per kilowatt in early 2025. Beyond supply chain constraints, regulatory delays have also added to project uncertainty. Even when projects secure every permit and complete regulatory reviews, federal courts can issue injunctions that stall or block construction, driving up costs and discouraging investment. The National Environmental Policy Act, a frequent target of litigation, further increases this risk by allowing lawsuits over minor procedural issues to delay projects indefinitely. As a result, investors and developers have become hesitant to commit financing over the last few years, even as demand for electricity from AI data centers and EVs continues to grow.
Other Reading…
Analyzing the Scale of Federal Layoffs in Trump’s First 100 Days (CNN)
Revenue from Customs Duties Hit New High as Trump Tariffs Take Effect (Bloomberg)
Americans Are Downbeat on the Economy. They Keep Spending Anyway (WSJ)
A Reckoning for Magnificent Seven Tests the Market (WSJ)
The H20 Problem: Inference, Supercomputers, and Export Control Gaps (Institute for Progress)
China’s Huawei Develops New AI Chip Seeking to Match Nvidia (WSJ)
GPU Price Tracker and Historical Trends for the Most Popular GPUs (United Compute)
Stripe Tests New Stablecoin Project as $3.7T Market Looms (Coindesk)

On X…
I think the Venturebeat article is very useful, most likely not for the vast majority of the people who read this weekly but for the vast majority of people using AI model providers. They typically don’t think about which provider solves their challenge. They rather are using a provider that is marketed best to them. It’s very interesting to think about how the industry is evolving to the consumer.
Teen innovators build saltwater-powered fridge that is changing the world https://www.americaoutloud.news/teen-innovators-build-saltwater-powered-fridge-that-is-changing-the-world/
If Deporting MS-13 Gang Members is a Constitutional Crisis, Then Let the Crisis Begin. https://torrancestephensphd.substack.com/p/if-deporting-ms-13-gang-members-is










