Neurosymbolic AI is the answer to large language models' inability ...
The main problem with big tech’s experiment with artificial intelligence (AI) is not that it could take over humanity. It’s that large language models (LLMs) like Open AI’s ChatGPT, Google’s Gemini, and Meta’s Llama continue to get things wrong, and the problem is intractable. Known as hallucinations, the most prominent example was perhaps the case of US law professor Jonathan Turley, who was falsely accused of sexual harassment by ChatGPT in 2023.
Challenges with Current Large Language Models
OpenAI’s solution seems to have been to basically “disappear” Turley by programming ChatGPT to say it can’t respond to questions about him, which is clearly not a fair or satisfactory solution. Trying to solve hallucinations after the event and case by case is clearly not the way to go.
The same can be said of LLMs amplifying stereotypes or giving western-centric answers. There’s also a total lack of accountability in the face of this widespread misinformation, since it’s difficult to ascertain how the LLM reached this conclusion in the first place.
The Emergence of Neurosymbolic AI

We saw a fierce debate about these problems after the 2023 release of GPT-4, the most recent major paradigm in OpenAI’s LLM development. Arguably the debate has cooled since then, though without justification.
The EU passed its AI Act in record time in 2024, for instance, in a bid to be a world leader in overseeing this field. But the act relies heavily on AI companies to regulate themselves without really addressing the issues in question.
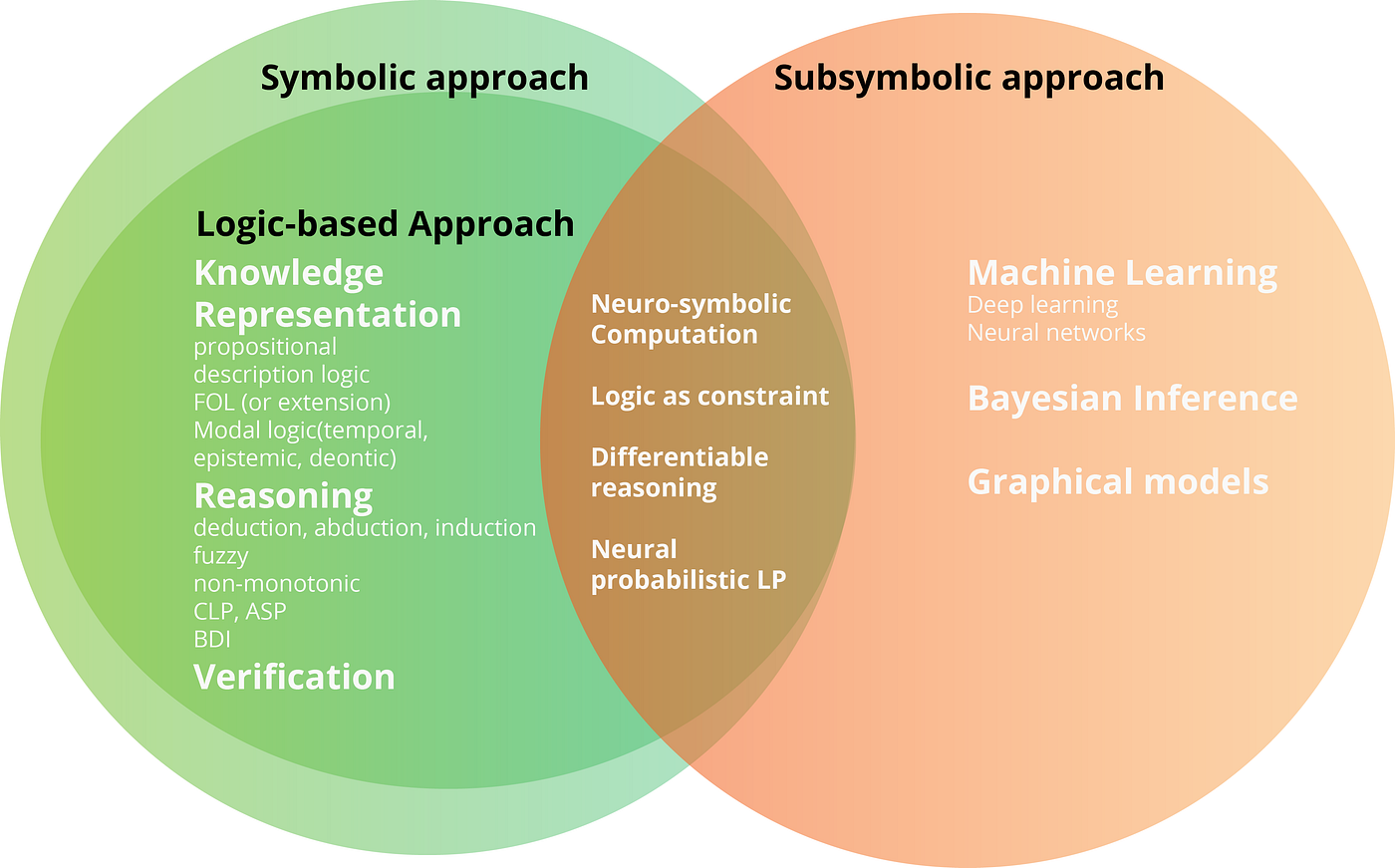
The emerging field of neurosymbolic AI could solve these issues, while also reducing the enormous amounts of data required for training LLMs. Neurosymbolic AI combines the predictive learning of neural networks with teaching the AI a series of formal rules that humans learn to be able to deliberate more reliably.
How Does Neurosymbolic AI Work?
LLMs work using a technique called deep learning, where they are given vast amounts of text data and use advanced statistics to infer patterns that determine what the next word or phrase in any given response should be. Each model – along with all the patterns it has learned – is stored in arrays of powerful computers in large data centers known as neural networks.
LLMs can appear to reason using a process called chain-of-thought, where they generate multi-step responses that mimic how humans might logically arrive at a conclusion, based on patterns seen in the training data.
Undoubtedly, LLMs are a great engineering achievement. They are impressive at summarizing text and translating but have the potential to mislead because their conclusions are always based on probabilities – not understanding.
Advantages of Neurosymbolic AI
Neurosymbolic AI integrates learning and formal reasoning, making it more energy efficient and accountable. It can follow pre-existing rules and ensure fair decision-making processes.
The first wave of AI in the 1980s, known as symbolic AI, laid the foundation for neurosymbolic AI as the third wave of AI development.
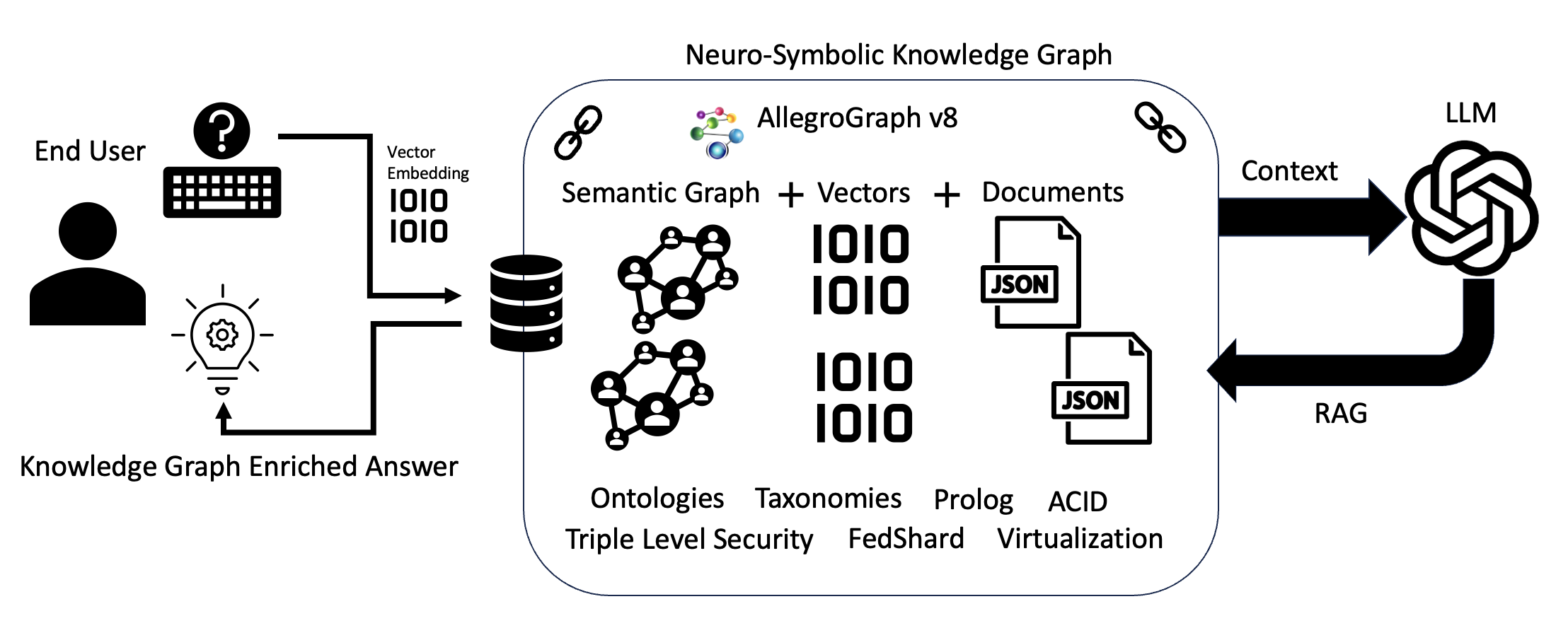
For more broad-based AIs, China’s DeepSeek uses a learning technique called “distillation” which is a step in the same direction. But to make neurosymbolic AI fully feasible for general models, there still needs to be more research to refine their ability to discern general rules and perform knowledge extraction.
Future of AI with Neurosymbolic Principles
If AI is going to keep advancing, we will need systems that adapt to novelty, check their understanding, multitask, and reason reliably in sophisticated ways. Well-designed digital technology could offer an alternative to regulation by building checks and balances into the architecture.
There’s a long way to go, but neurosymbolic AI presents a promising path forward.




















