China Ramping Renewables & Slamming Brakes On Coal Could ...
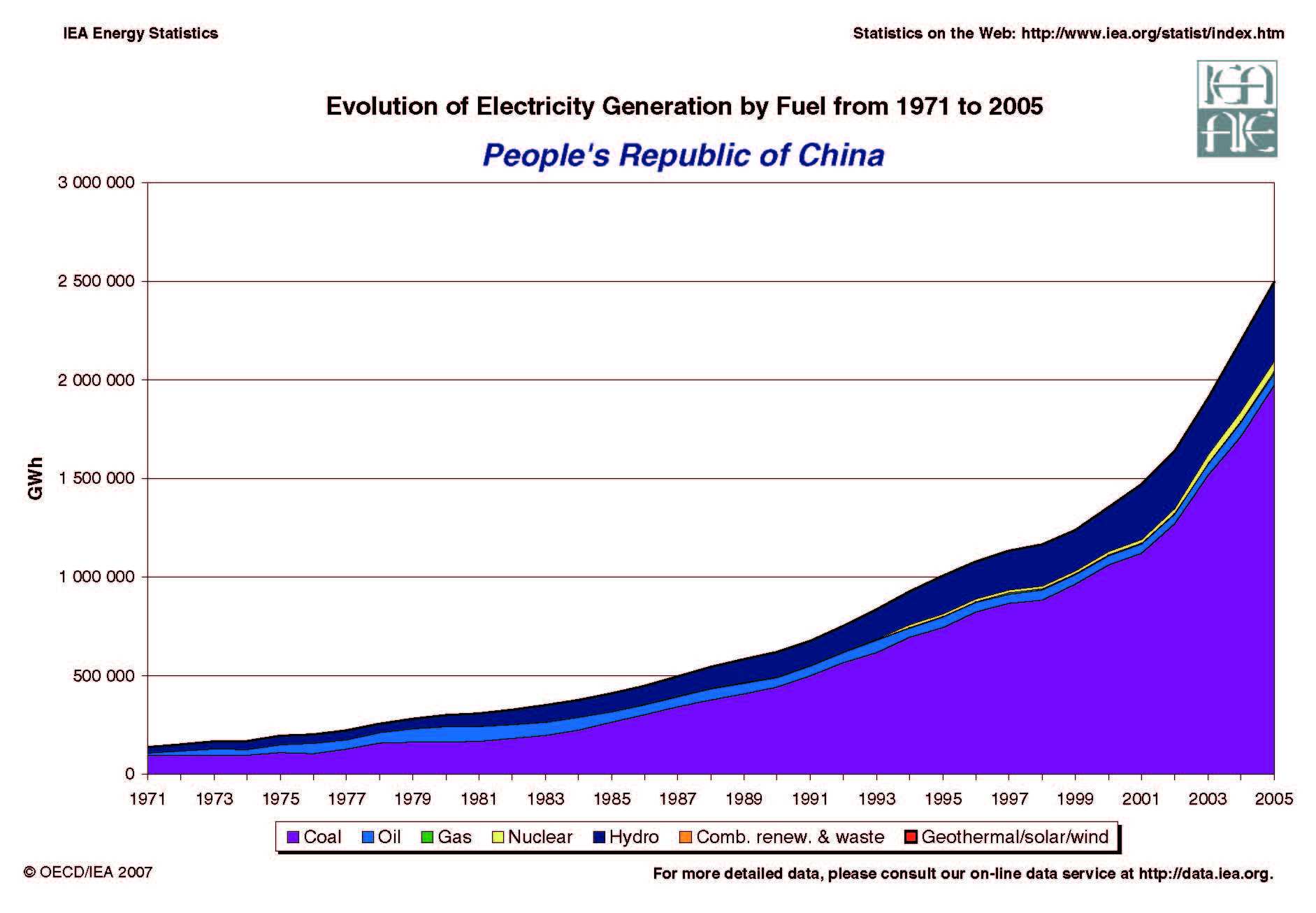
China's coal generation continues to be a topic of interest globally due to its massive carbon dioxide emissions. In the past year alone, emissions from coal in China amounted to over 6.1 billion tons, surpassing the combined emissions from global aviation and shipping sectors. The spotlight recently has been on China's significant decrease in new coal plant licensing, with only 10 GW permitted in the first half of 2024, marking an 83% drop. Additionally, China's coal capacity factors are on the decline while wind and solar installations set new annual records.

New Generation Trends
China has been gradually shutting down older coal plants and replacing them with modern supercritical plants that burn cleaner coal, leading to reduced carbon dioxide emissions. Currently, over 40% of China's coal fleet consists of modern supercritical plants that utilize high-grade, low-sulfur coal sourced domestically.
Progress in Renewable Energy
On the other hand, China has made substantial strides in renewable energy, connecting 274 GW of wind and solar power to the grid in 2023, setting a new record. Projections suggest that by 2030, wind and solar energy could contribute over 40% to China's electrical supply, while coal's share might decrease to around 34%. Nuclear power generation is expected to see minimal growth, with the construction of new nuclear plants having a limited impact on the overall energy mix.
Impact on CO2 Emissions
As China continues to transition towards cleaner energy sources, there is a noticeable reduction in carbon dioxide emissions from the electrical generation sector. The shift towards renewables and the decline in coal generation could potentially lower global carbon emissions by around 15% in the next seven years.

China's emphasis on electrification and the rapid growth of renewable energy sectors position the country as a leader in energy efficiency and carbon reduction. By decarbonizing its electricity with affordable renewables, China gains a competitive advantage in energy costs and carbon footprint compared to other regions.
Looking Ahead
China's commitment to scaling low-carbon technologies and driving climate action through massive deployment sets a precedent for other nations. By prioritizing renewable energy and reducing reliance on coal, China is forging a path towards a more sustainable and environmentally conscious future.




















