How AI Music & Voice Generation Models Work
The lines between art and technology are blurring. Machine learning models are rapidly advancing new tools for text, music, or image creation. And it’s not happening in isolation – exciting outcomes are emerging when these areas begin to connect. From text-to-speech narrations to visual art that changes based on sound and music, AI is creating more dynamic and engaging experiences.
AI Models for Sound and Voice Generation
In this article, we are exploring how AI models generate a variety of content forms – specifically sound and voice. We’ll explain how different generative models are learning to speak, sing, and create tunes that are not only unique but also quite realistic. It's no longer just sci-fi. The future of sound and voice generation is already here, and there is one question we have yet to answer — are we ready for the challenges that come with the sound transformation? Let’s find out!
Types of Sound and Voice Generation Models
Sound and voice generative models use machine learning techniques and a vast amount of training audio data to create new audio content. You can create custom sound effects, music, and even realistic human speech.
Background and Ambient Noises
Generative models can be great for creating background noises for games, videos, and other production scenarios. The main training data they use are nature soundscapes, traffic noise, crowds, machinery, and other ambient environments.

Music Generation
If you’re a musician who’s stuck on a melody and needs a little bit of push, you can use AI to either create new pieces or finish the existing ones based on your preferences. For this specific modeling process, trainers use large datasets of existing music grouped together based on their unique genres, including instrumental, vocal, and musical notes.
Text-to-Speech
Text-to-speech is another great example of what can be done with AI sound and voice generation models. It allows you to create different voices. As you can imagine, the training data for this particular format is mainly recordings of human voices speaking in different languages, accents, and emotional tones.
Digital Representation of Sounds
To create new sounds or voices, generative models analyze large datasets of sounds represented by either waveforms or spectrograms and find patterns in them during the training process. Essentially, there are two main ways to represent sounds digitally: waveforms and spectrograms.
Waveforms
Waveforms or sound waves are raw representations of sound with two parameters -- time and amplitude, the height of the wave defining its loudness. If you zoom in on an image of a waveform, you’ll see points (samples) on the plot describing time and amplitude. These points define a waveform itself. Each dot in a waveform represents a sound sample. Waveforms are heavy in terms of data that needs to be processed since each second may require from 44,000 to 96,000 samples, depending on the sound quality you’re looking for.
Spectrograms
Spectrograms are another way to visually and digitally represent sounds. Unlike waveforms, spectrograms have three parameters of sound: time, frequency, and amplitude. They show how loud the sound is at each frequency at each moment of time. This representation requires less data and computation resources for model training.
A spectrogram of a person talking. Source: Wikimedia
So, spectrograms are also a common way to train both sound generation and sound recognition models.
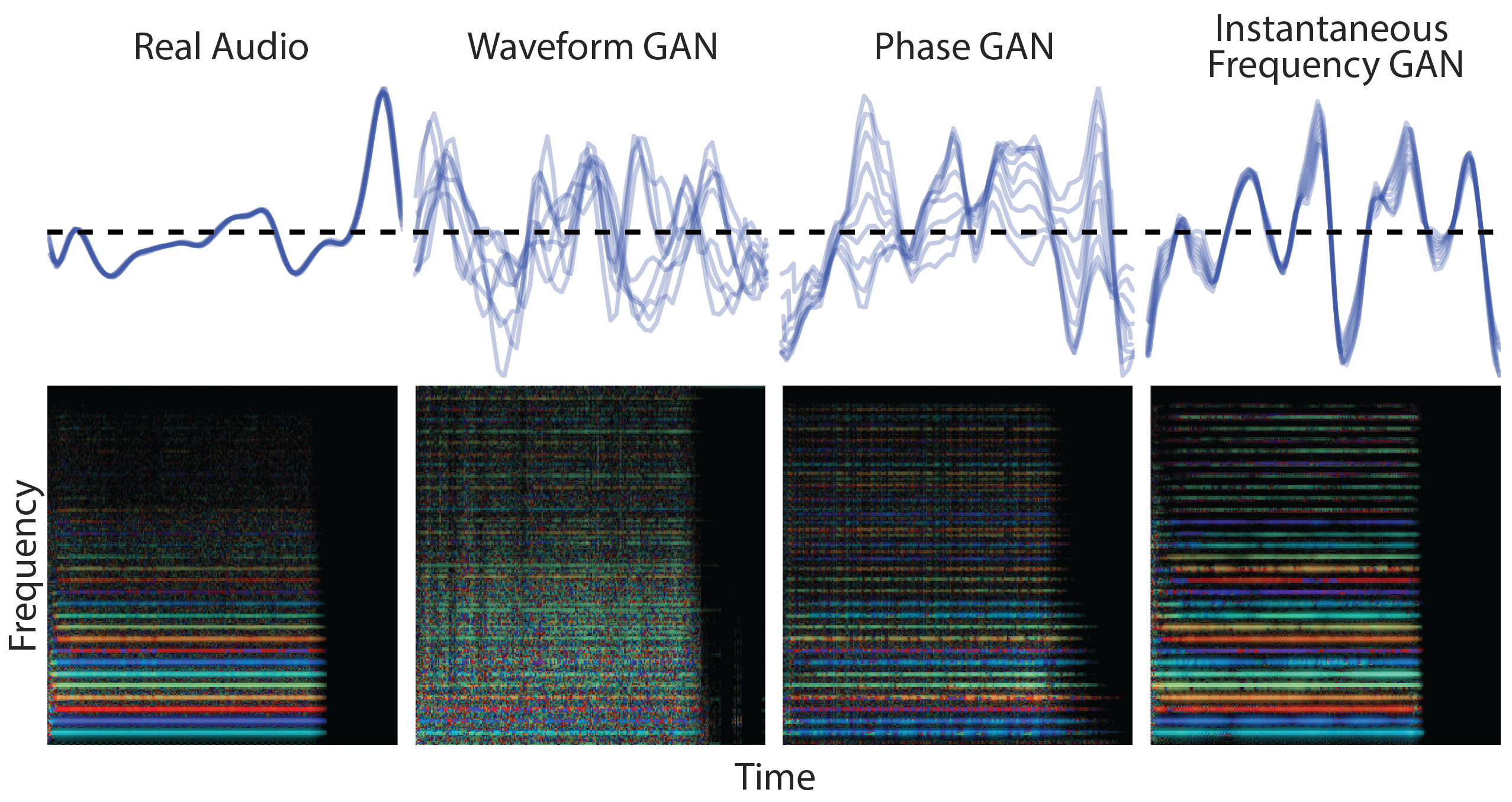
Generative Machine Learning Models
Once the model has learned relationships and patterns of sounds by looking at such features as frequency, time, and amplitude, it can use this knowledge to create entirely new waveforms and spectrograms. There are several main types of generative machine learning models used for sound generation, including autoregressive models, variational autoencoders (VAEs), generative adversarial networks (GANs), and transformers.
Autoregressive Models
An autoregressive model predicts the next part in a sequence by analyzing and taking into account the previous elements. Autoregressive models are normally used to create statistical predictions on time series. They forecast natural phenomena, economic processes, and other events that change over time.




















