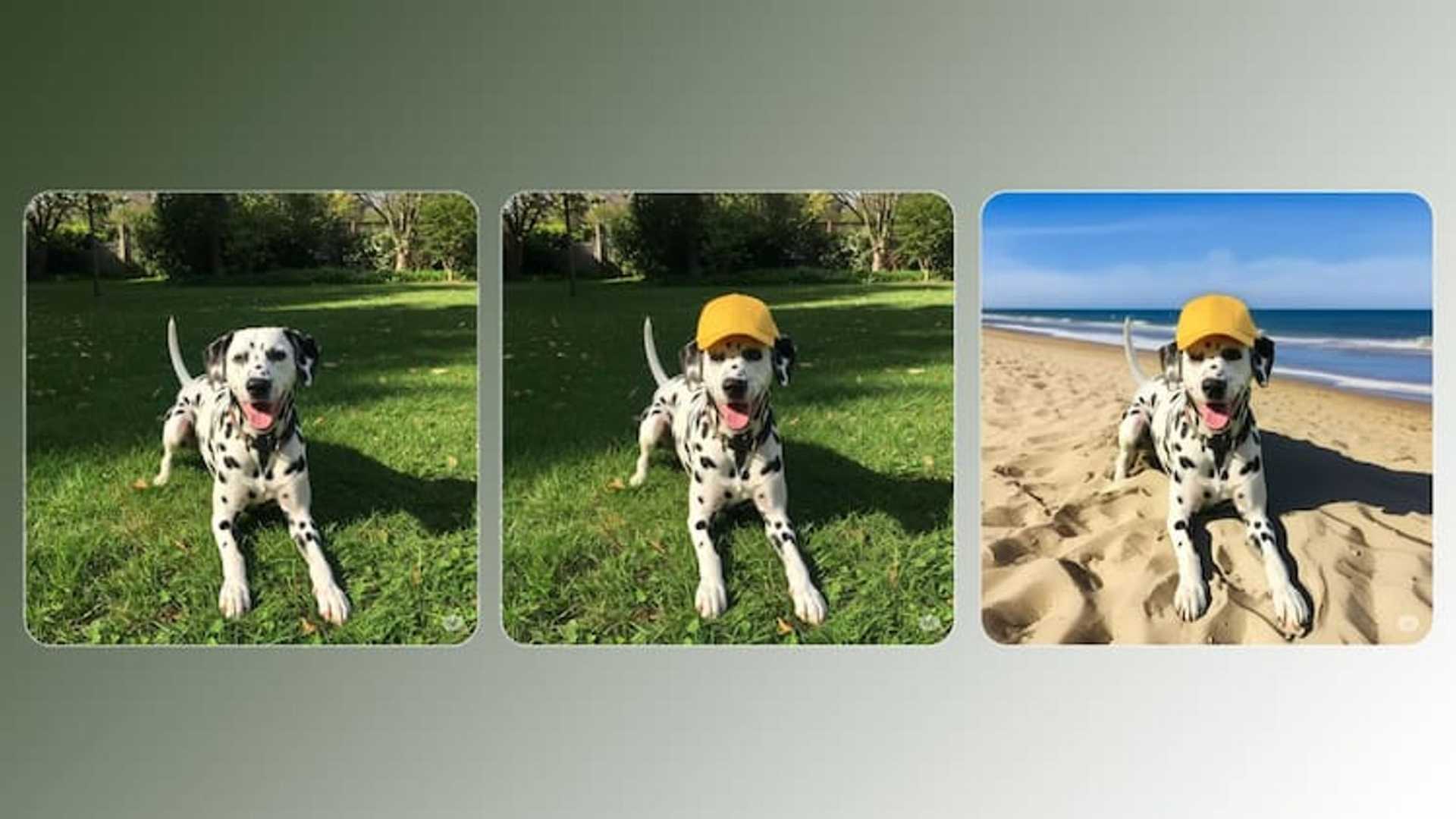
If I forgive, negotiate, show compassion, mercy to AI employees, AI investors, AI leaders, AI managers, CEOs, CTOs, CHROs, CIOs, CFOs, CROs, board members, air conditioning, HVAC, refrigeration, autom...
Reactive machines are the most basic forms of AI, designed to respond to specific situations or stimuli without any memory of past experiences. They function by reacting to inputs with predetermined outputs, like a chess-playing AI that can’t learn from past games.
Limited memory AI involves AI systems that can use recent or short-term data to make decisions. Unlike reactive machines, they have a temporary memory, which allows them to adapt their responses based on recent information, like a self-driving car adjusting its actions based on recent traffic data.
Theory of Mind AI, a more advanced form of AI, would be capable of understanding and interpreting human emotions, beliefs, and intentions, and then responding in a contextually appropriate manner. It’s about AI that can function in social contexts in a way that shows an understanding of human psychological states.
Theory of Mind AI aims to understand human emotions, beliefs, intentions, and desires. While this type of AI remains in development, it would allow machines to engage in more sophisticated interactions by perceiving emotions and adjusting behavior accordingly.
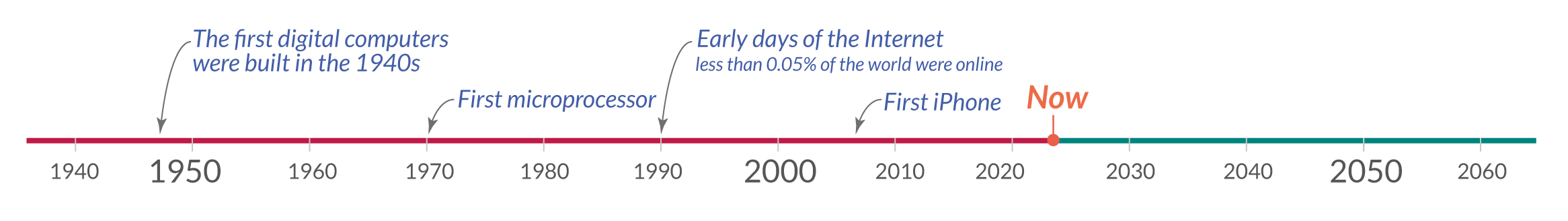
The brief history of artificial intelligence: the world has ...
Self-aware AI is a hypothetical, future form of AI that would possess its own consciousness and self-awareness. Such AI would not only understand its environment and interact intelligently but also have an understanding of itself as an entity—its own thoughts, feelings, and desires.
Chapter - Data Visualization | Bentham Science

Symbolic AI operates on the principles of logic and rules. This type of AI uses symbols to represent problems and applies a set of predefined rules to manipulate these symbols and derive conclusions or actions. It’s akin to solving problems using a complex flowchart, where each decision leads to a specific outcome based on rules.
Connectionist AI, using artificial neural networks, simulates the human brain’s structure to learn and make decisions by analyzing data, identifying patterns, and making inferences. This approach contrasts with Symbolic AI’s rule-based system, offering adaptability and proficiency in handling complex, real-world situations. Connectionist AI is the foundation of most modern AI advancements, including progress in natural language processing, image and speech recognition, and predictive analytics. Its learning capability has made it central to cutting-edge AI applications, driving much of the field’s current excitement and investment.
Evolutionary AI
Inspired by biological evolution, Evolutionary AI employs algorithms that mimic natural selection processes. These algorithms use mutation, crossover, and selection to evolve solutions over generations. They start with random solutions and iteratively evolve these towards better performance, guided by a fitness function. Evolutionary AI’s innovations are diverse but useful in optimizing systems and evolving designs for complex problems. It thrives in environments with vast, ambiguous solution spaces, useful in robotic control, game strategy, and optimization challenges. Its adaptability and creative problem-solving approach make it a valuable tool for tackling multifaceted issues.
Applications of AI in Various Industries
Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, AI is revolutionizing the way care is delivered. AI-driven systems are being used for more accurate diagnoses, often identifying conditions from images like X-rays and MRIs with a precision that matches or exceeds that of human experts. In treatment planning, AI algorithms can analyze data from numerous cases to suggest personalized treatment plans for patients, considering factors that might be overlooked by humans. Moreover, AI is at the forefront of personalized medicine, tailoring healthcare to the individual’s genetic makeup, lifestyle, and other factors.
Finance
The finance industry has embraced AI for a range of applications. AI systems are instrumental in detecting fraudulent transactions by analyzing patterns and identifying anomalies that deviate from usual behavior. In trading, AI algorithms can process vast amounts of market data to identify trends and execute trades at optimal times, often faster than human traders could manage. Risk analysis is another area where AI excels, helping financial institutions assess the creditworthiness of borrowers and the risk levels of various investment options by analyzing complex datasets.
Self-aware AI
Self-aware AI is still one of the theoretical types of artificial intelligence. It’s about AI that doesn’t just process data or understand emotions but is aware of its own existence.
Theory of Mind AI: Understanding Minds, Not Just Data
Theory of Mind AI represents a leap forward from the ‘learning from data’ approach. It’s an AI that’s not just processing information and making decisions based on data; it’s about understanding and interacting with emotions, beliefs, thoughts, and expectations. Essentially, it’s AI that seeks to understand the human mind.
The Human Connection
The key idea here is empathy and social understanding. Imagine a robot or a digital assistant that doesn’t just respond to your commands but understands your feelings and can adapt its responses accordingly.
Potential Applications:
Self-Aware AI is an advanced stage of AI that possesses self-consciousness and awareness. This type of AI would have the ability to not only understand and react to emotions but also have its own consciousness, similar to human awareness. While we are far from achieving self-aware AI, it remains the ultimate goal for AI development. It opens philosophical debates about consciousness, identity, and the rights of AI systems if they ever reach this level.
Artificial Deep Reasoning in AGI & Superintelligence | by Rob ...

Artificial Superintelligence is like a computer program that can be smarter than people. It learns and thinks by itself. Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a widely talked-about topic in today’s rapidly changing world.
Theory of Mind AI
Theory of Mind AI is still one of the theoretical types of artificial intelligence. It is where artificial intelligence starts crossing over from purely technical territory into something that feels straight out of a sci-fi novel.
Potential Applications:
Artificial Superintelligence is like a computer program that can be smarter than people. It learns and thinks by itself. Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a widely talked-about topic in today’s rapidly changing world.
The top-down approach to creating artificial superintelligence involves starting from the desired goals or functions of intelligence. These goals will differ based on the organization or person and can involve reasoning, learning, or problem-solving to achieve them. Superintelligence would have the ability to analyze patterns and predict future events with remarkable accuracy. It could forecast trends in finance, climate change, or human behavior, enhancing decision-making in these areas.
Artificial Intelligence is based on human insights that can be decided in a way that can machine can effortlessly actualize the tasks, from the basic to those that are indeed more complex. The reason for manufactured insights is learning, problem-solving, reasoning, and perception. This term may be connected to any machines which show related to a human intellect such as examination and decision-making and increments the efficiency. AI covers assignments like robotics, control systems, face recognition, scheduling, data mining, and numerous others.
In today’s tech-driven world, machines are being designed to mimic human intelligence and actions. One key aspect of this is reasoning, a logical process that enables machines to conclude, make predictions, and solve problems just like humans. Artificial Intelligence (AI) employs various types of reasoning to achieve this, including expert systems, natural language processing, speech recognition, and computer vision. Reasoning can be defined as the logical process of drawing conclusions, making predictions, or constructing solutions based on existing knowledge. In Artificial Intelligence, reasoning plays a crucial role in understanding how the human brain thinks, draws conclusions, and solves problems. Through reasoning, AI systems can simulate human-like decision-making and problem-solving capabilities. Let’s dive into the different types of reasoning used in AI.
Deductive reasoning follows a top-down approach where conclusions are drawn from general principles or premises that are known or assumed to be true. This form of reasoning relies on established facts to infer valid conclusions. Deductive reasoning is often used in expert systems and rule-based AI systems, where knowledge is represented through rules (if-then statements). These systems apply general rules to specific problems to derive solutions or make decisions.
Inductive reasoning is a bottom-up approach that involves drawing general conclusions from specific instances or observations. Unlike deductive reasoning, inductive reasoning generates hypotheses rather than certain conclusions, making it more probabilistic. If we observe that the sun rises in the east every day, we may infer that the sun will rise in the east tomorrow. Inductive reasoning is widely used in machine learning algorithms. Models trained on data patterns generalize from the data and use this information to make predictions about new, unseen data.
Abductive reasoning starts with an incomplete set of observations and then seeks the most plausible explanation. It focuses on finding the most likely conclusion based on what is known, rather than seeking an absolute truth. If a patient has a fever and cough, a doctor might hypothesize that they have the flu, even though other illnesses could cause similar symptoms.










