In Today's AI Race, Don't Gamble with Your Digital Privacy | Beebom
Living in the AI age means being constantly surrounded by chatbots and AI-driven services. As AI continues to integrate into every aspect of our lives, data collection by AI companies becomes more and more prevalent. While this data is crucial for training AI models, it also raises concerns about personal privacy. To navigate this landscape, it is essential to understand the privacy policies of popular AI services and take necessary steps to safeguard your digital privacy.
Google's Gemini and Privacy Concerns
Google's Gemini, a prominent AI chatbot, automatically stores all user activity data without explicit consent. Conversations on Gemini are not only stored for up to 18 months but are also processed by human reviewers to enhance Google's AI model. While Google claims to anonymize data to protect user privacy, certain information like location details, IP addresses, and device type are retained as part of Gemini Apps activity. Users are advised not to share sensitive or personal information to prevent unauthorized access.

Despite offering the option to disable Gemini Apps activity and delete related data, Google retains conversations evaluated by human reviewers for up to three years. Additionally, even when the activity is turned off, conversations are stored for 72 hours for service provision and feedback processing.
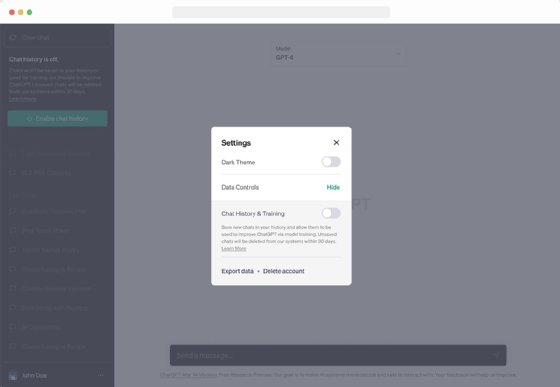
OpenAI's ChatGPT and Addressing Privacy
OpenAI's ChatGPT, a widely used AI chatbot, similarly saves all conversations by default. While users are cautioned against sharing sensitive information, the lack of clear disclosure regarding data usage on the homepage raises transparency concerns. Personal data collected by ChatGPT includes conversations, images, files, and content from Dall-E for model improvement.
Users can disable chat history and training in ChatGPT settings, but this preference does not sync across devices. Chat history is retained for 30 days for monitoring purposes but is excluded from model training.
Microsoft Copilot and Privacy Challenges
Microsoft Copilot's privacy policy lacks transparency regarding data collection and handling practices. While users can disable personalization and clear activity history, the absence of clear settings within Copilot raises concerns.
Copilot Pro users' data from Office apps may be used for new AI experiences, which can be disabled through Account Privacy settings. However, the specific personal data collected by Copilot and its handling remain ambiguous.
Ensuring Privacy in the AI Landscape
As users engage with AI tools and services, particularly those processing personal data, understanding data retention policies and privacy controls is crucial. Opting for AI image tools that can run locally, like SuperImage and Upscayl, provides an alternative to cloud-based services.
Furthermore, assessing data sharing practices with third parties is essential. While Google and OpenAI have distinct approaches to data sharing, ensuring data security and privacy protection remains a shared responsibility between users and AI service providers.
Risks of Data Privacy Violations
The integration of personal data into AI training datasets poses inherent risks to individual privacy and data security. Unauthorized data access and potential data breaches can compromise user confidentiality and trust in AI services. Transparent communication of privacy policies and data usage practices is essential to establish user trust and mitigate privacy concerns in the evolving AI landscape.










