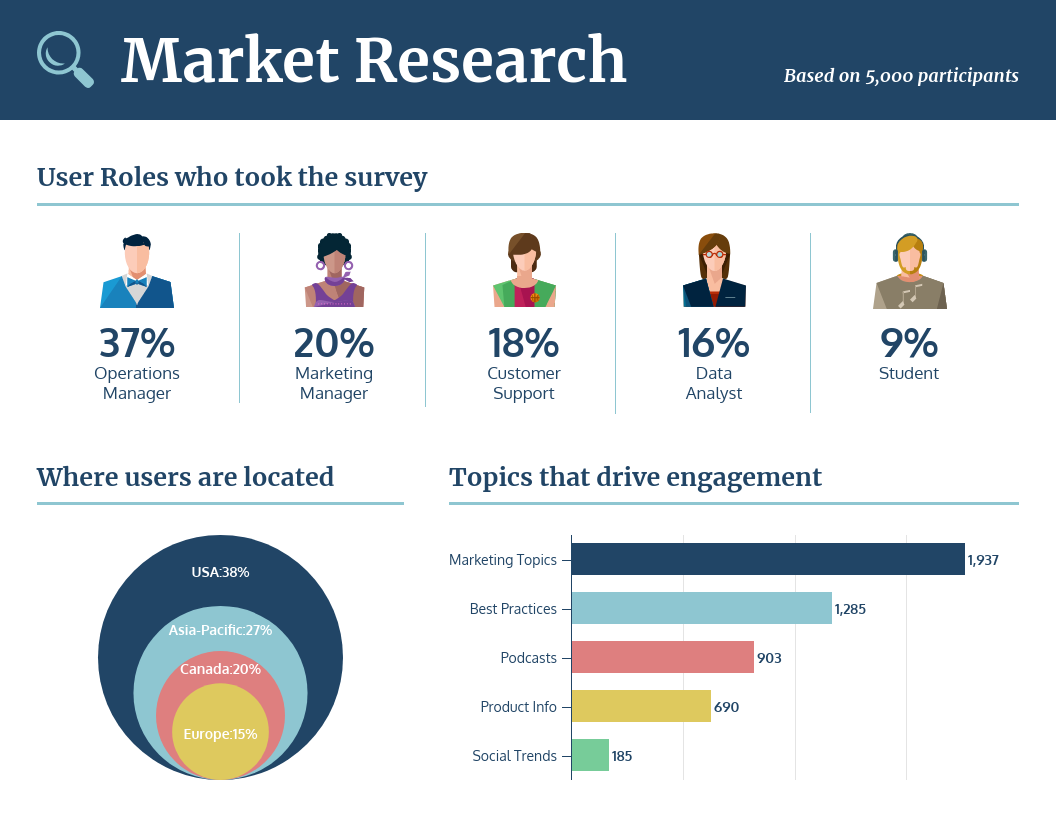
Investigating Factors Behind User Trust in ChatGPT
ChatGPT, developed by OpenAI, is a versatile tool that can handle various tasks, from entertainment to healthcare queries. It can summarize large volumes of text, generate programming code, and assist with certain healthcare tasks. However, despite its benefits, there are significant risks that can hinder its adoption in high-risk domains.
These risks include potential inaccuracies, ethical issues such as copyright and plagiarism, hallucination (producing false but plausible information), and biases from its pre-2021 training data. To address these risks, it is recommended to use ChatGPT for tasks that humans can accurately supervise. Studies suggest that using ChatGPT under human oversight can help mitigate risks and ensure critical decisions remain human-made.
Factors Influencing User Trust in ChatGPT: A Conceptual Framework
User trust in ChatGPT is crucial and depends on its perceived accuracy and reliability. Positive user experiences can enhance trust and satisfaction, while inaccuracies can erode trust. A conceptual framework based on established technology acceptance theories explores factors influencing user trust in ChatGPT, including performance expectancy, workload, satisfaction, risk-benefit perception, and trust.
The framework hypothesizes that understanding these factors can aid in effectively integrating ChatGPT into various sectors by balancing its capabilities with informed user expectations.
Image Credit: Digital.gov
Surveying User Perceptions: Methodology and Constructs
A recent study published in JMIR Human Factors aimed to explore how perceived workload, satisfaction, performance expectancy, and risk-benefit perception influence users' trust in ChatGPT. The study utilized a semistructured, web-based questionnaire distributed to U.S. adults who used ChatGPT (version 3.5) at least once a month.
The survey focused on five constructs: trust, workload, performance expectancy, satisfaction, and risk-benefit perception, with responses measured on a 4-point Likert scale. The survey provided insights into user behavior and model validation, highlighting the significance of factors such as performance expectancy, satisfaction, workload, and risk-benefit perceptions in influencing trust in ChatGPT.
Human Factors and Implications for Responsible AI
This study is among the first to explore how human factors such as workload, performance expectancy, risk-benefit perception, and satisfaction influence trust in ChatGPT. The results indicate that these factors significantly impact trust, with performance expectancy exerting the strongest influence.
Reducing user workload is vital for enhancing satisfaction, which in turn improves trust in ChatGPT. The study's findings align with efforts to advance responsible AI research and emphasize the importance of creating trustworthy AI systems. Future research should focus on longitudinal designs and include diverse user perspectives to deepen the understanding of trust in AI technologies.
Source: JMIR Human Factors











