Large Language Models in Biomedicine
Large language models such as GPT-4 have been making significant strides in various industries, with biomedicine being no exception. A recent study conducted by a research team from MedUni Vienna’s Institute of Artificial Intelligence and the CeMM Research Center for Molecular Medicine, led by Matthias Samwald and Christoph Bock, has unveiled the potential of using GPT-4 as a powerful simulator for biological systems.
Enhancing Biological Simulation with GPT-4
The study aimed to explore the efficacy of utilizing GPT-4 for the stepwise simulation of biological and medical processes. The findings suggest that this approach could yield superior results, paving the way for enhanced applications in biomedical research and a deeper understanding of these innovative models.
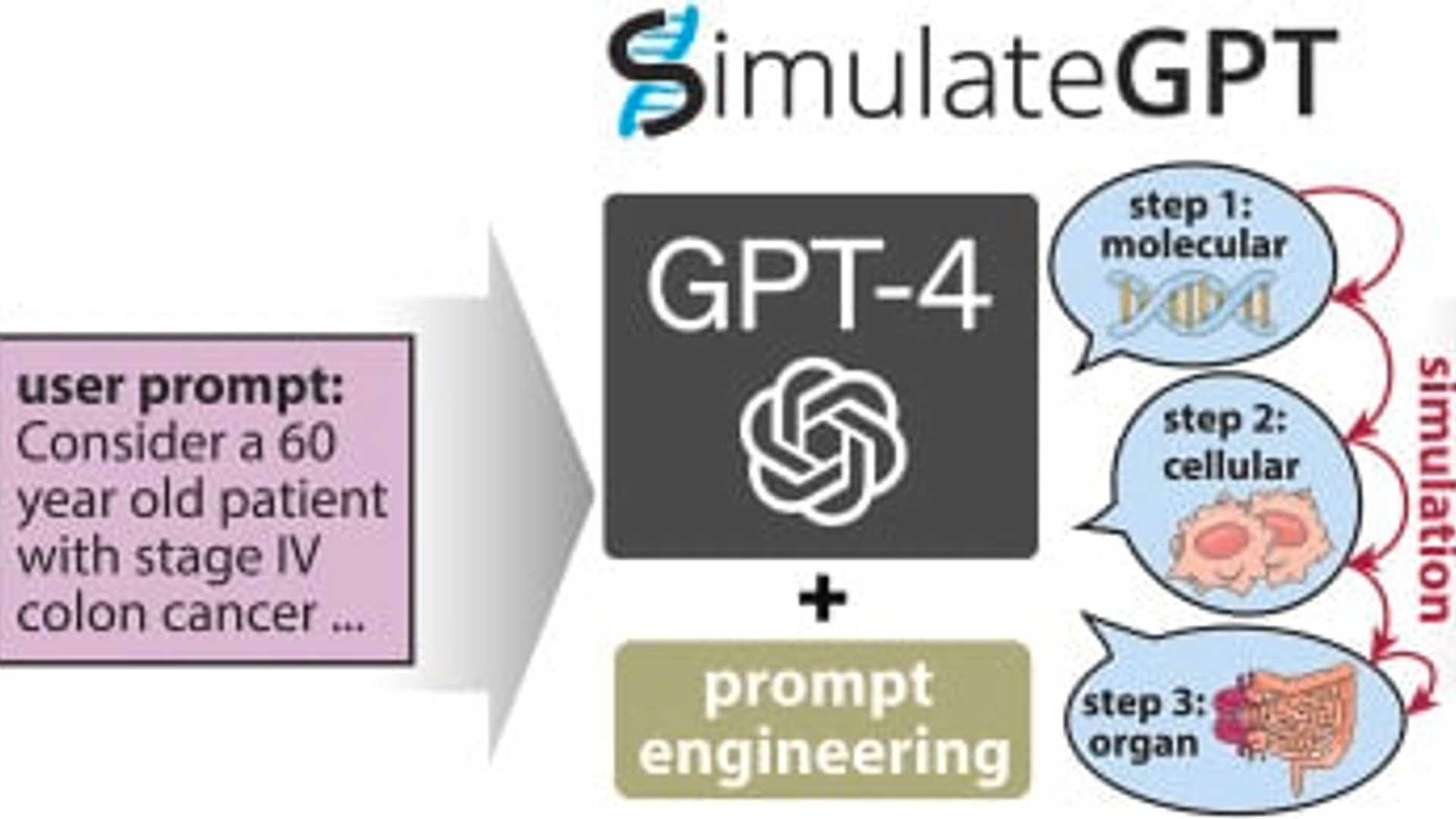
Introducing SimulateGPT
The experiments conducted during the study highlighted a preference among biomedical experts for SimulateGPT's predictions over direct GPT-4 responses. Moreover, SimulateGPT exhibited improved accuracy in identifying crucial genes in cancer cells and predicting cancer patients' progression-free survival rates.

Driving Biomedical Insights with Text-based Models
Language models like GPT-4 rely on text prompts to execute specific tasks or tackle problems. While models such as ChatGPT/GPT-4 excel at straightforward queries, they encounter difficulties in handling the complexity of biomedicine. By configuring GPT-4 with structured inputs and targeted instructions, researchers were able to simulate intricate scenarios effectively. The study showcased the enhanced performance of this GPT-4-based simulator in comparison to conventional approaches.
Empowering Biomedical Simulations
Traditional computer simulations of biological processes often demand substantial expertise and manual fine-tuning. To address this challenge, the research team introduced "SimulateGPT," a knowledge-based simulation technique that leverages structured inputs within the GPT-4 framework. This method was rigorously tested and validated across various scenarios, ranging from mouse experiments to sepsis treatment support and the prediction of essential genes in cancer cells.
Future Implications and Recommendations
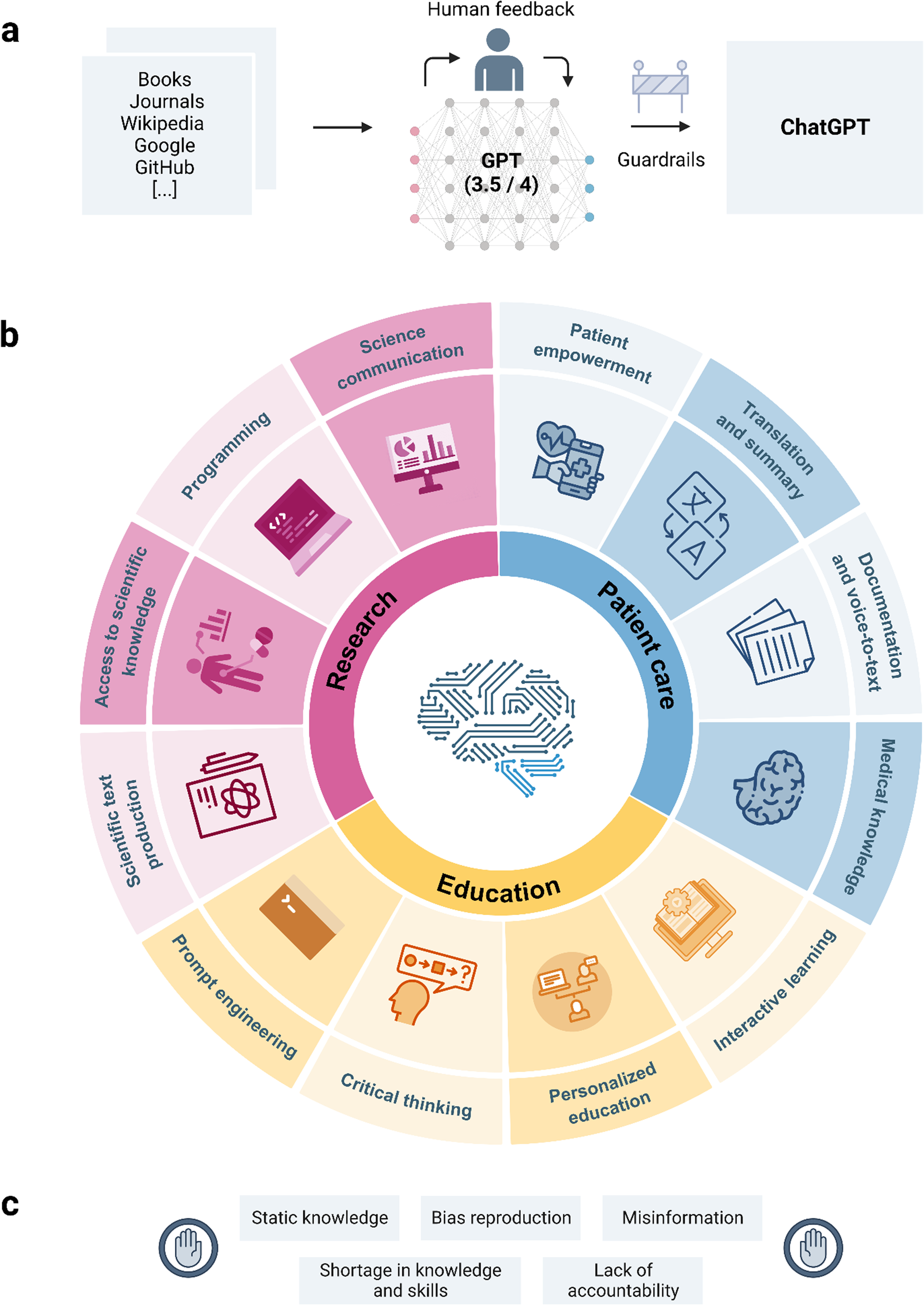
Matthias Samwald emphasized the transformative potential of large language models like GPT-4 in advancing biomedical simulations. Text-based approaches offer a versatile and interpretable means of modeling complex biological systems. The study advocates for the integration of biological databases, mathematical modeling, and training new AI models with experimental data to further refine LLM-based biomedical simulators.

For more details, you can access the original story here.