Good Fire AI Open-Sources Sparse Autoencoders (SAEs) for Llama ...
Large language models (LLMs) like OpenAI’s GPT and Meta’s LLaMA have significantly advanced natural language understanding and text generation. However, these advancements come with substantial computational and storage requirements, making it challenging for organizations with limited resources to deploy and fine-tune such massive models. Issues like memory efficiency, inference speed, and accessibility remain significant hurdles.
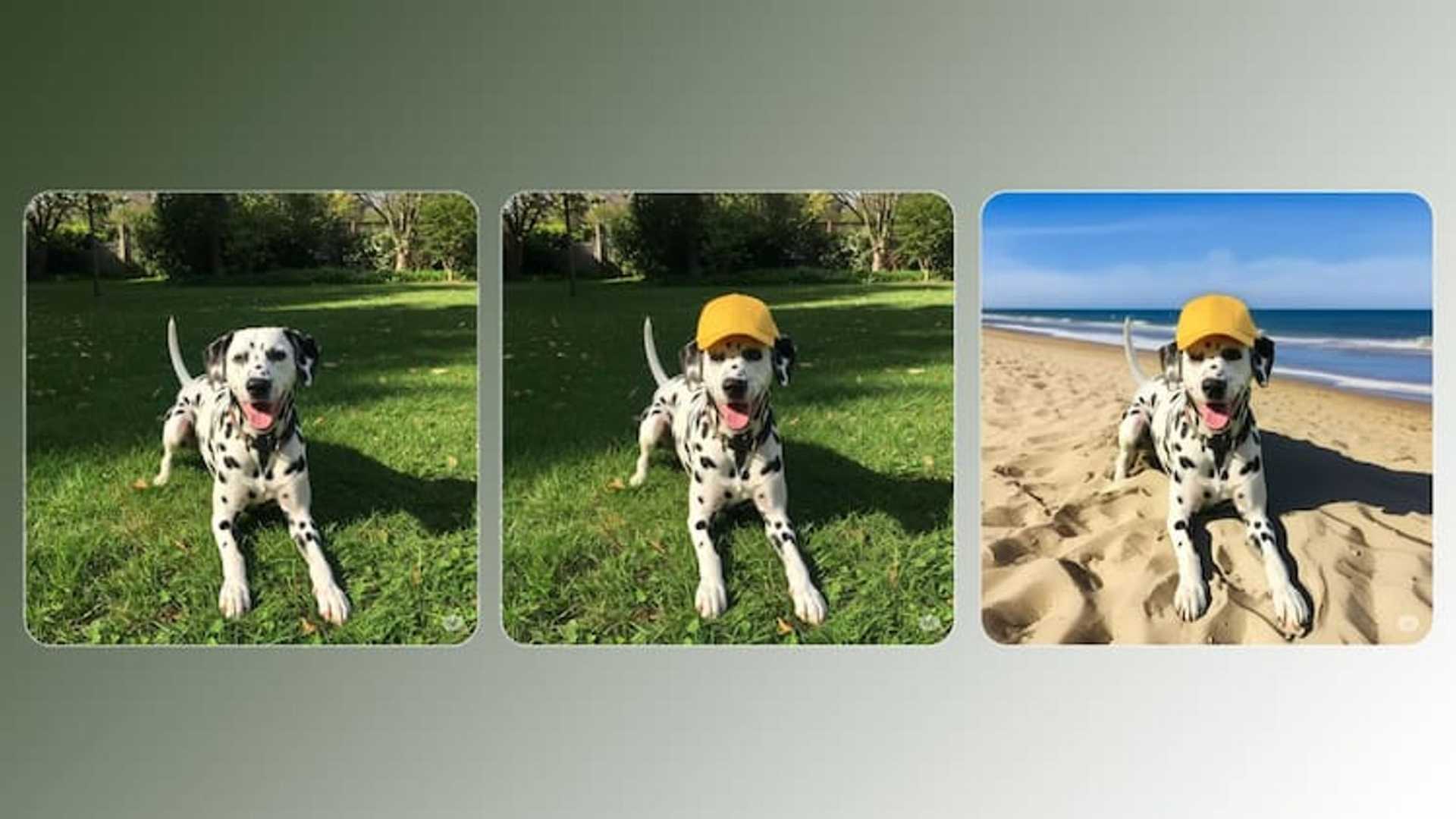
Good Fire AI has introduced a practical solution by open-sourcing Sparse Autoencoders (SAEs) for Llama 3.1 8B and Llama 3.3 70B. These tools utilize sparsity to improve the efficiency of large-scale language models while maintaining their performance, making advanced AI more accessible to researchers and developers.
Enhancing Efficiency with Sparse Autoencoders
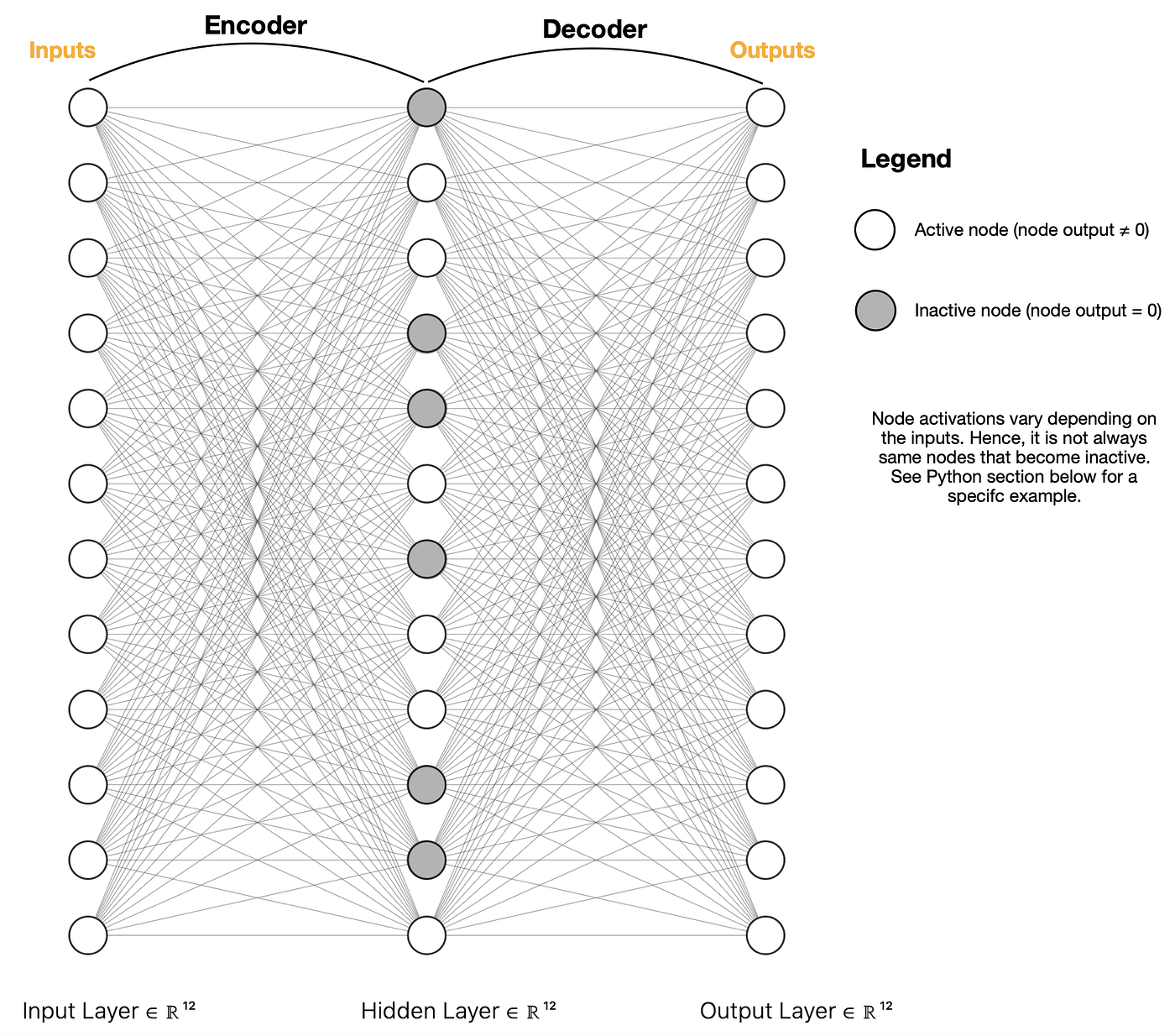
Good Fire AI’s SAEs are designed to enhance the efficiency of Meta’s LLaMA models, focusing on two configurations: LLaMA 3.3 70B and LLaMA 3.1 8B. Sparse Autoencoders leverage sparsity principles, reducing the number of non-zero parameters in a model while retaining essential information.
The open-source release provides pre-trained SAEs that integrate smoothly with the LLaMA architecture. These tools enable compression, memory optimization, and faster inference. By hosting the project on Hugging Face, Good Fire AI ensures that it is accessible to the global AI community. Comprehensive documentation and examples support users in adopting these tools effectively.
Advantages of Sparse Autoencoders for LLaMA Models
SAEs encode input representations into a lower-dimensional space while preserving the ability to reconstruct data with high fidelity. Sparsity constraints allow these autoencoders to retain the most critical features, eliminating redundant elements. When applied to LLaMA models, SAEs offer several advantages:
- Sparsity-inducing penalties during training
- Optimized decoding mechanisms for output quality
- Fine-tuning for specific instruction-following tasks
Results shared by Good Fire AI highlight the effectiveness of SAEs. The LLaMA 3.1 8B model with sparse autoencoding achieved a 30% reduction in memory usage and a 20% improvement in inference speed compared to its dense counterpart, with minimal performance trade-offs. Similarly, the LLaMA 3.3 70B model showed a 35% reduction in parameter activity while retaining over 98% accuracy on benchmark datasets.
Tangible Benefits and Applications
These results demonstrate tangible benefits in natural language processing tasks, where the sparse models performed competitively in metrics like perplexity and BLEU scores, supporting applications such as summarization, translation, and question answering. Additionally, Good Fire AI’s Hugging Face repositories provide detailed comparisons and interactive demos, promoting transparency and reproducibility.
Driving Innovation in AI Technology
Good Fire AI’s Sparse Autoencoders offer a meaningful solution to the challenges of deploying large language models. By improving memory efficiency, inference speed, and accessibility, SAEs help make advanced AI tools more practical and inclusive. The open-sourcing of these tools for LLaMA 3.3 70B and LLaMA 3.1 8B provides researchers and developers with resources to implement cutting-edge models on constrained systems.
As AI technology progresses, innovations like SAEs will play a vital role in creating sustainable and widely accessible solutions. For those interested, the SAEs and their LLaMA integrations are available on Hugging Face, supported by detailed documentation and an engaged community.










