Can ChatGPT Replace Google Search? 2025 AI Search Engine ...
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape of 2025, the way we seek and consume information online is undergoing a profound transformation. For years, Google Search has been the undisputed titan, the go-to platform for billions seeking answers, websites, and data. However, with the meteoric rise of sophisticated AI chatbots like OpenAI’s ChatGPT, a fundamental question has emerged: Can ChatGPT replace Google Search? This isn’t just a theoretical debate; recent estimates show hundreds of millions are using ChatGPT weekly for diverse tasks, including information retrieval.
Core Differences: ChatGPT vs. Google Search
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape of 2025, the way we seek and consume information online is undergoing a profound transformation. For years, Google Search has been the undisputed titan, the go-to platform for billions seeking answers, websites, and data. However, with the meteoric rise of sophisticated AI chatbots like OpenAI’s ChatGPT, a fundamental question has emerged: Can ChatGPT replace Google Search? This isn’t just a theoretical debate; recent estimates show hundreds of millions are using ChatGPT weekly for diverse tasks, including information retrieval.
At their core, ChatGPT and Google Search are designed with fundamentally different architectures and intended purposes for information retrieval. Google Search operates as an expansive index of the internet. When a user enters a query, Google’s complex algorithms scour its index to find relevant web pages, then ranks and presents them as a list of links. Its primary function is to direct users to existing information sources across the web.
Conversely, ChatGPT, a large language model developed by OpenAI, is built for conversational interaction and content synthesis. Trained on a massive dataset of text and code, it generates responses by predicting the next word in a sequence based on the input prompt. While it can access and process information it was trained on, its strength lies in understanding context, generating human-like text, summarizing information, and engaging in dialogue, rather than providing direct, real-time links to external websites. This difference in design dictates their respective strengths and weaknesses in the context of online search.
Strengths and Limitations
ChatGPT excels in scenarios where the user’s information need is exploratory, ambiguous, or requires synthesized answers rather than a list of links. Its conversational interface allows users to refine queries iteratively, ask follow-up questions naturally, and explore topics from various angles. This makes it particularly effective for tasks like brainstorming ideas, understanding complex concepts by requesting simplified explanations, or drafting initial content based on gathered information.
Users often find ChatGPT more convenient for obtaining quick, summarized answers, especially when they prioritize ease of access over the need to verify information across multiple sources. The absence of advertisements and the streamlined interface provide a friction-free experience compared to navigating traditional search results pages. For many, obtaining an answer that is “good enough” rapidly within a single conversational flow is preferable to sifting through numerous links.
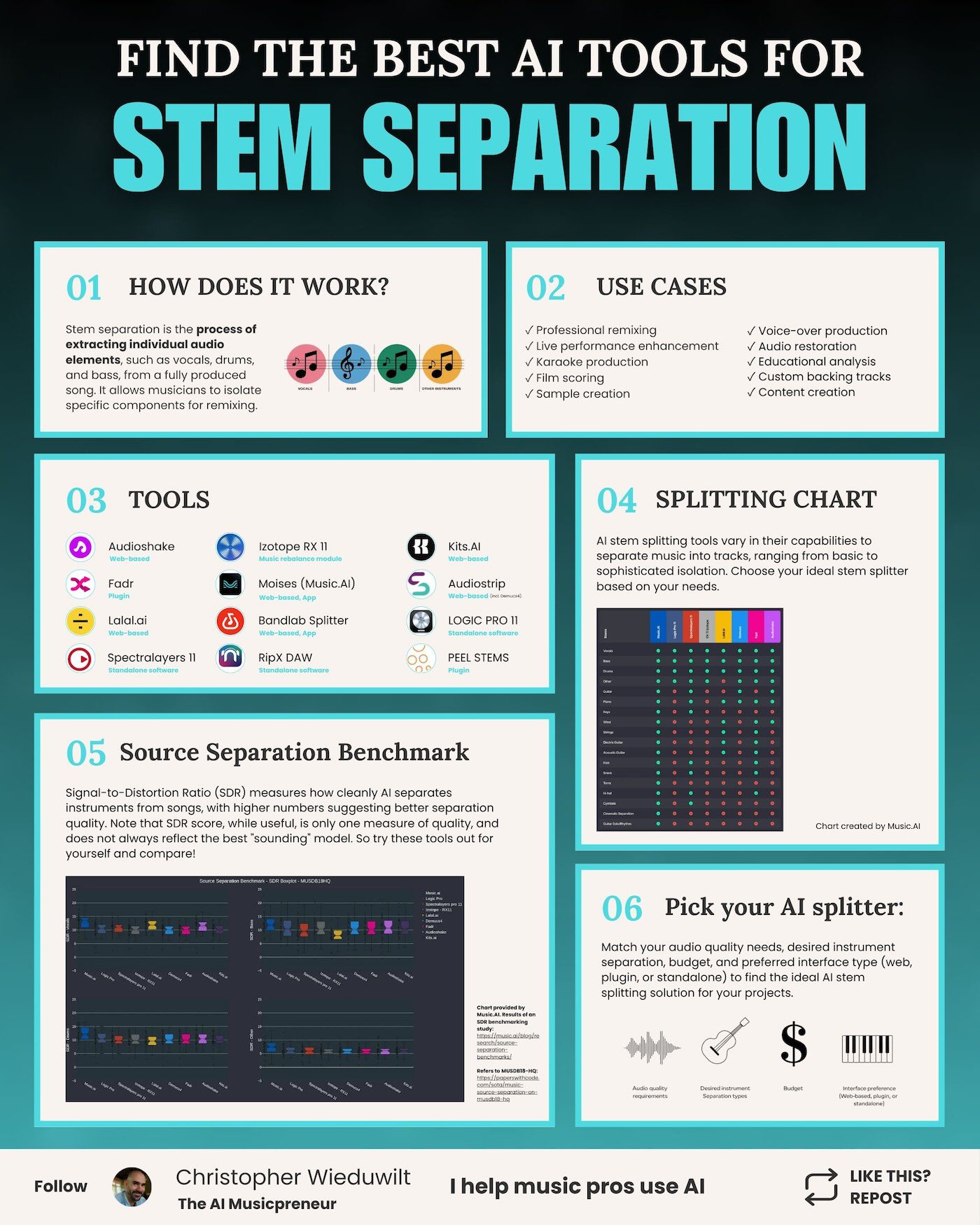
Preference for Specific Use Cases
| Use Case | Preferred Tool | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Finding a specific website | Google Search | Direct indexing, speed, links to original source. |
| Checking real-time news | Google Search | Access to up-to-date, indexed web content. |
| Researching complex topic | ChatGPT | Summarization, explanation, conversational refinement of understanding. |
| Brainstorming ideas | ChatGPT | Generative capability, exploring different perspectives conversationally. |
| Fact-checking information | Google Search | Provides multiple sources for cross-verification. |
| Quick definition lookup | Either | Both can provide definitions, but Google links to authoritative sources. |
| Planning a trip (exploratory) | ChatGPT | Can suggest ideas, structure plans, and answer broad questions initially. |
Future Outlook and Implications
Despite the rise of conversational AI, Google Search maintains its position as the dominant force in online information retrieval for several critical reasons. Its sheer scale and sophisticated indexing capabilities mean it provides access to a vast and constantly updated repository of web pages, offering unparalleled breadth and depth of information.
Recognizing the shift in user expectations brought about by conversational AI, Google has been aggressively integrating its own advanced AI models into its core search product. The integration of features like AI Overviews aims to provide summarized answers directly at the top of the search results page, competing with ChatGPT’s core strength in summarization.
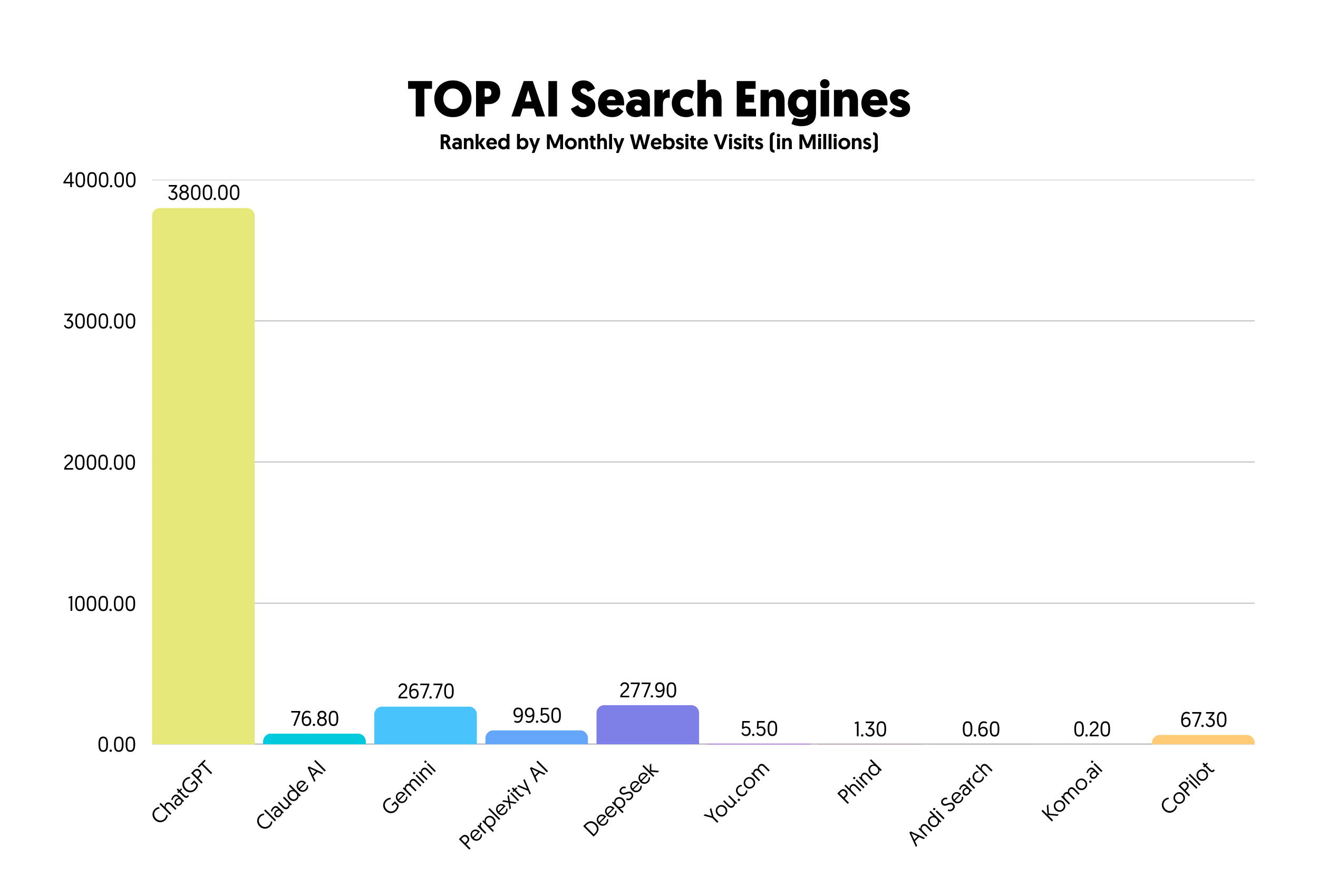
While ChatGPT offers compelling advantages for certain tasks, it comes with notable limitations for information retrieval, particularly concerning accuracy and access to real-time information. A significant challenge is the phenomenon of “AI hallucinations,” where the model generates confidently false or nonsensical information.
Content Strategies and User Interaction
The shift towards AI Overviews and synthesized chatbot responses poses challenges for publishers and website owners who rely on search engine traffic. Business models reliant solely on high-volume, low-intent search traffic are particularly vulnerable. Navigating this evolving environment requires publishers to innovate and diversify their audience engagement and revenue streams.
Convergence and Co-existence
The current trajectory suggests that the future of AI search engines is less about one tool completely replacing the other and more about convergence and co-existence. Users are increasingly leveraging both tools based on the nature of their information needs, sometimes even in tandem for a more effective workflow.
| Feature | Google Search (with AI) | ChatGPT |
|---|---|---|
| Core Mechanism | Indexing & Ranking (enhanced by AI synthesis) | Large Language Model (Generative & |










