Exploring Multimodal LLMs: Techniques and Models
The field of artificial intelligence is constantly evolving, pushing the boundaries of what machines can achieve. One of the recent exciting developments is the emergence of multimodal Large Language Models (LLMs). These models go beyond just processing text; they have the ability to integrate and analyze various data inputs like images, audio, and videos to produce text as an output.

A notable example of this advancement is Meta AI's Llama 3.2 models, which have set a new benchmark in AI capabilities. In this article, we will delve into the world of multimodal LLMs, exploring their techniques, models, and the revolutionary potential they offer across various industries.
Techniques of Multimodal LLMs
Multimodal LLMs represent a significant leap from traditional language models due to their ability to handle diverse data modalities. They excel in tasks such as image captioning and converting structured data into different formats like LaTeX or Markdown.

There are two primary approaches in developing multimodal LLMs:
Unified Embedding Decoder Approach
In this approach, a single decoder model processes concatenated token embeddings from text and images. The images are divided into patches and encoded using a Vision Transformer (ViT), allowing for seamless integration of image data into text-based models.
This architecture is beneficial for applications requiring real-time agent assistance and rapid data processing.
Cross-Modality Attention Approach
Unlike the unified architecture, this approach processes image patches separately within a multi-head attention layer using a cross-attention mechanism. It efficiently links image and text embeddings, making it ideal for applications needing a deep understanding of both visual and textual data.
Models and Innovations
The introduction of models like Llama 3.2 showcases a trend towards more integrated systems using open-weight models. Innovations such as the Fuyu model highlight efforts to simplify architectures and streamline training processes, shaping the future of AI in business.
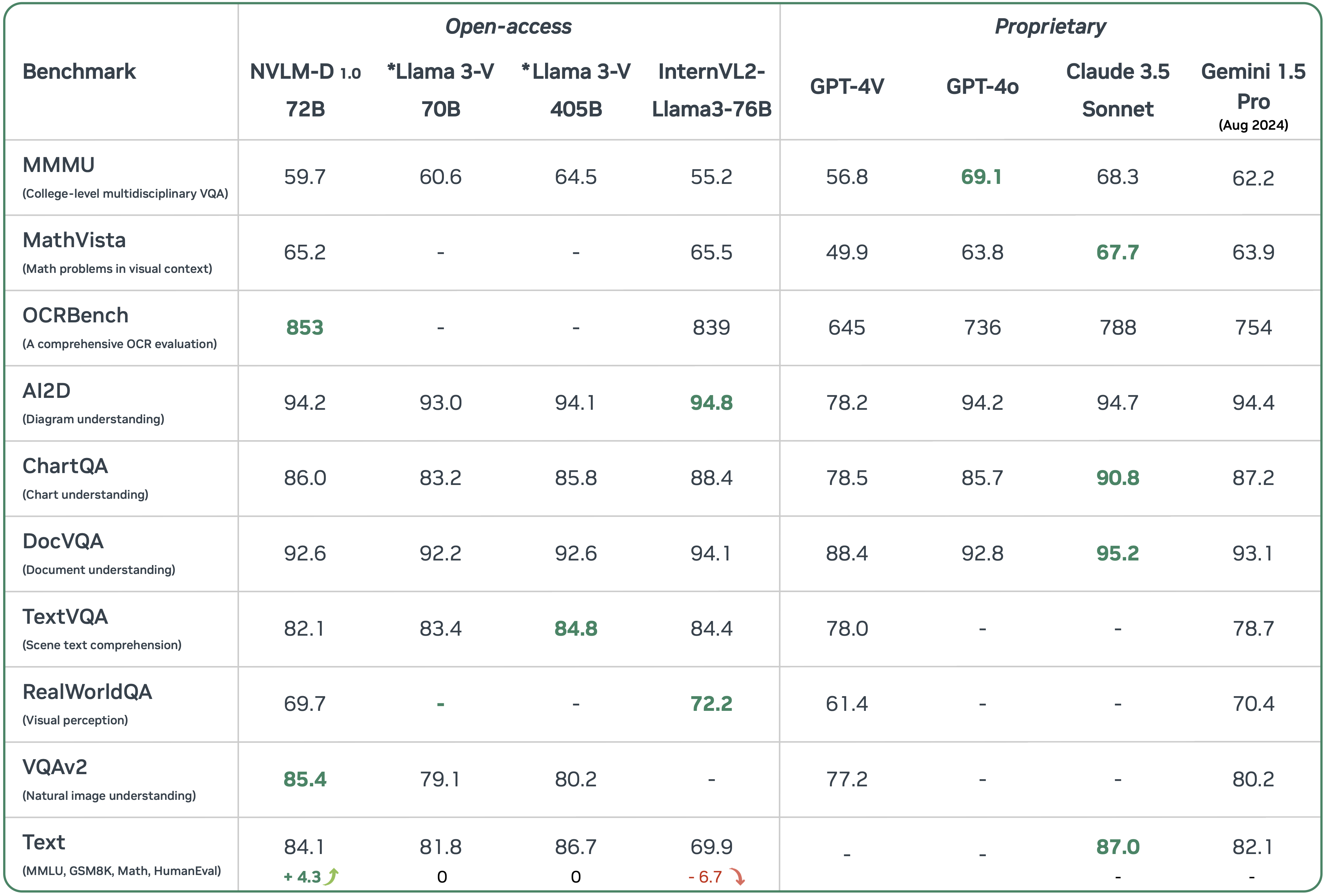
These models promise enhanced capabilities for data analysis across multiple input forms, leading to improved efficiency and effectiveness in real-world applications.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Challenges may arise in training models that operate directly on image patches without traditional image encoders, including managing complexity and ensuring accurate interpretation of visual data.
Models like Llama 3.2 with open-weight versions could influence future AI research by making advanced capabilities more accessible, fostering innovation and development of new applications.